CentOS6.3下GitLab+Nginx(SSL)+MySQL+Ruby安装部署
Gitlab是一个用Ruby on Rails开发的开源项目管理程序.可以通过WEB界面进行访问公开的或者私人项目. 它和Github有类似的功能,能够浏览源代码,管理缺陷和注释.
本文选择NGINX与MYSQL来配合GitLab实现web管理,数据存储等功能,配置过程中难点基本在GitLab的脚本修改,SSH秘钥连接,Nginx SSL证书等这些方面,作者也是耗费非常大的力气,结合很多文档的clue以及很多老外的debug comment,终于最终完成,希望在此给大家一个抛砖引玉的机会,了解到SCM(软件配置管理)其实也不是想象中那么小儿科,很多逻辑也着实需要下功夫investigation.
最后我是一路向北,我为我自己带盐....
解决方案:
环境部署
操作系统 centos6.3 x64
GitLab GitLab 6-3-stable
GitLab Shell 1.8.0
Ruby 2.0.0p353
NGINX nginx-1.4.0
MYSQL mysql-5.6.10
Git server(centos6.3 x64): git.example.com
Git client(centos6.3 x64): client.example.com
server端配置:
一.安装前的准备工作
1.关闭iptables和SELINUX
# service iptables stop
# setenforce 0
# vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux
---------------
SELINUX=disabled
---------------
2.同步时间
# ntpdate cn.pool.ntp.org
3.安装LNMP
传送门:http://www.showerlee.com/archives/73
4.安装GitLab的所需依赖包和工具
# su -
# rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
# yum -y groupinstall 'Development Tools'
# yum -y install vim-enhanced readline readline-devel ncurses-devel gdbm-devel glibc-devel tcl-devel openssl-devel curl-devel expat-devel db4-devel byacc sqlite-devel gcc-c++ libyaml libyaml-devel libffi libffi-devel libxml2 libxml2-devel libxslt libxslt-devel libicu libicu-devel system-config-firewall-tui python-devel redis sudo wget crontabs logwatch logrotate perl-Time-HiRes git
5.配置redis
配置redis开机启动:
# chkconfig redis on
# service redis start
6.更改gem源(若默认无法连接)
a.显示当前使用的sources
# gem sources
b.删除缺省source
# gem sources -r http://rubygems.org/
c.添加一个source
# gem sources -a http://ruby.taobao.org
d.更新source cache
# gem sources -u
6.安装Ruby
a.源码安装Ruby
传送门: http://www.showerlee.com/archives/1123
b.安装bundle组件:
# gem install bundler --no-ri --no-rdoc
二.安装GITLab shell
1.创建用户git
# su -
# adduser --system --shell /bin/bash --comment 'GitLab' --create-home --home-dir /home/git/ git
2、配置GitLab shell
GitLab shell是专门为GitLab开发的提供ssh访问和版本管理的软件。
a.使用git账户登陆
# su - git
b.克隆gitlab shell
# git clone https://github.com/gitlabhq/gitlab-shell.git
c.切换成1.8.0版本,并编辑配置
# cd gitlab-shell
# git checkout v1.8.0
d.拷贝配置文件
# cp config.yml.example config.yml
# vi config.yml
—————————————————————————————————————————
# 将gitlab_url修改成gitlab的访问域名。例如本文档:https://git.example.com/
gitlab_url: "https://git.example.com"
# 将self_signed_cert修改成 true
self_signed_cert: true
# 添加网站SSL证书
ca_file: "/usr/local/nginx/ssl/gitlab.crt"
—————————————————————————————————————————
注:如果gitlab是使用http访问,则需将https替换成http,配置文件中的self_signed_cert要修改成false,否则gitlab shell在通过api和gitlab进行通信的时候就会出现错误,导致项目push出错。因为后面配置web服务器的时候是使用ssl,所以这里要按照ssl的方式配置。
另外本文档的域名为测试域名,不要忘记在C/S两端均做好域名映射。
e.安装一些需要的目录和文件
# ./bin/install
5、配置MySQL数据库(安装过程详见上文)
a.登录数据库
# mysql -u root -p
b. 为gitlab创建使用用户
> create user gitlab@'localhost' identified by '123456';
c.创建gitlaba使用的数据库
> CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `gitlabhq_production` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET `utf8` COLLATE `utf8_unicode_ci`;
d.给予gitlab用户权限
> GRANT SELECT, LOCK TABLES, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP, INDEX, ALTER ON `gitlabhq_production`.* TO 'gitlab'@'localhost';
三.安装GitLab
1.将GitLab安装在git的家目录下:
# su - git
2.克隆GitLab并切换分支到6-3-stable
a.克隆GitLab
# git clone https://github.com/gitlabhq/gitlabhq.git gitlab
b. 切换到6-3-stable分支
# cd /home/git/gitlab
# git checkout 6-3-stable
c、配置项目
a.复制配置文件
# cp config/gitlab.yml.example config/gitlab.yml
b.修改配置文件中的访问域名
# sed -i 's|localhost|git.example.com|g' config/gitlab.yml
d.设定log和tmp目录所有者和权限
# chown -R git log/
# chown -R git tmp/
# chmod -R u+rwX log/
# chmod -R u+rwX tmp/
e.创建gitlab-satellites目录
# mkdir /home/git/gitlab-satellites
f.创建tmp/pids/和tmp/sockets/目录,确保gitlab有相应的权限
# mkdir tmp/pids/
# mkdir tmp/sockets/
# chmod -R u+rwX tmp/pids/
# chmod -R u+rwX tmp/sockets/
g.创建public/uploads目录
# mkdir public/uploads
# chmod -R u+rwX public/uploads
h.复制unicorn配置
# cp config/unicorn.rb.example config/unicorn.rb
i.保持unicorn配置文件默认配置
g.配置git的用户和邮件
# git config --global user.name "GitLab"
# git config --global user.email "gitlab@git.example.com”
# git config --global core.autocrlf input
k.配置数据库访问文件
# cp config/database.yml.mysql config/database.yml
编辑config/database.yml,设置其中连接数据库的账号密码
# vi config/database.yml
———————————————————————————————————
#
# PRODUCTION
#
production:
adapter: mysql2
encoding: utf8
reconnect: false
database: gitlabhq_production
pool: 10
username: gitlab
password: “123456”
# host: localhost
# socket: /tmp/mysql.sock
———————————————————————————————————
修改其中username和password就可以了,其中密码就是上面数据库步骤中创建gitlab用户的密码。
l.确保该文件只有git账号有权限读取。
# chmod o-rwx config/database.yml
四.安装Gems
1.安装charlock_holmes
# su -
# gem install charlock_holmes --version '0.6.9.4'
# exit
2.安装mysql包
# cd /home/git/gitlab/
# vi Gemfile
修改 https://rubygems.org 为 http://ruby.taobao.org
# bundle install --deployment --without development test postgres puma aws
若报Could not find modernizr-2.6.2 in any of the sources错误,没有则无视:
修复方案:
# vi Gemfile
搜索该行 gem "modernizr", "2.6.2"
更改为: gem "modernizr-rails", "2.7.1"
# vi Gemfile.lock
搜索该行 modernizr (2.6.2)
更改为: modernizr-rails (2.7.1)
搜索该行 modernizr (= 2.6.2):
更改为: modernizr-rails (= 2.7.1)
重新执行
# bundle install --deployment --without development test postgres puma aws
3.初始化数据和激活高级功能
# cd /home/git/gitlab
# bundle exec rake gitlab:setup RAILS_ENV=production
这步完成后,会生一个默认的管理员账号/密码:
admin@local.host/5iveL!fe
4.安装启动脚本
# su -
# wget -O /etc/init.d/gitlab https://raw.github.com/gitlabhq/gitlab-recipes/5-0-stable/init.d/gitlab
# chmod +x /etc/init.d/gitlab
5.开机时启动
# chkconfig --add gitlab
# chkconfig gitlab on
6.检测应用程序状态
# su - git
# cd gitlab/
# bundle exec rake gitlab:env:info RAILS_ENV=production
# exit
可以查看到系统、Ruby、GitLab和GitLab Shell的版本和其他信息。
7.启动GitLab实例
# service gitlab start
8.查看应用更加详细的信息
# su - git
# cd gitlab/
# bundle exec rake gitlab:check RAILS_ENV=production
这里会提示一个Init script up-to-date的错误,如下:
——————————————————————————————————————————————————
Init script up-to-date? ... no
Try fixing it:
Redownload the init script
For more information see:
doc/install/installation.md in section "Install Init Script"
Please fix the error above and rerun the checks.
——————————————————————————————————————————————————
查阅官方自带文档,说明此问题可忽略.
五.Nginx配置
1.配置Gitlab虚拟主机及SSL连接:
# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/vhosts/
# vi gitlab-ssl.conf
注: 这里先感谢提供此脚本的极客,该脚本在原基础上稍作改动.
内容用红字标注的地方为需要自定义的地方.
————————————————————————————————————————————
## GitLab
## Contributors: randx, yin8086, sashkab, orkoden, axilleas
## App Version: 5.4 - 6.0
##
## Modified from nginx http version
## Modified from http://blog.phusion.nl/2012/04/21/tutorial-setting-up-gitlab-on-debian-6/
##
## Lines starting with two hashes (##) are comments containing information
## for configuration. One hash (#) comments are actual configuration parameters
## which you can comment/uncomment to your liking.
##
###################################
## SSL configuration ##
###################################
##
## Optimal configuration is taken from:
## https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Strong_SSL_Security_On_nginx.html
## Make sure to read it and understand what each option does.
##
## [Optional] Generate a self-signed ssl certificate:
## mkdir /etc/nginx/ssl/
## cd /etc/nginx/ssl/
## sudo openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -x509 -nodes -days 3560 -out gitlab.crt -keyout gitlab.key
## sudo chmod o-r gitlab.key
##
## Edit `gitlab-shell/config.yml`:
## 1) Set "gitlab_url" param in `gitlab-shell/config.yml` to `https://git.example.com`
## 2) Set "ca_file" to `/etc/nginx/ssl/gitlab.crt`
## 3) Set "self_signed_cert" to `true`
## Edit `gitlab/config/gitlab.yml`:
## 1) Define port for http "port: 443"
## 2) Enable https "https: true"
## 3) Update ssl for gravatar "ssl_url: https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/%{hash}?s=%{size}&d;=mm"
##
##################################
## CHUNKED TRANSFER ##
##################################
##
## It is a known issue that Git-over-HTTP requires chunked transfer encoding [0]
## which is not supported by Nginx < 1.3.9 [1]. As a result, pushing a large object
## with Git (i.e. a single large file) can lead to a 411 error. In theory you can get
## around this by tweaking this configuration file and either:
## - installing an old version of Nginx with the chunkin module [2] compiled in, or
## - using a newer version of Nginx.
##
## At the time of writing we do not know if either of these theoretical solutions works. As a workaround
## users can use Git over SSH to push large files.
##
## [0] https://git.kernel.org/cgit/git/git.git/tree/Documentation/technical/http-protocol.txt#n99
## [1] https://github.com/agentzh/chunkin-nginx-module#status
## [2] https://github.com/agentzh/chunkin-nginx-module
upstream gitlab {
## Uncomment if you have set up puma/unicorn to listen on a unix socket (recommended).
server unix:/home/git/gitlab/tmp/sockets/gitlab.socket;
## Uncomment if puma/unicorn are configured to listen on a tcp port.
## Check the port number in /home/git/gitlab/config/{puma.rb/unicorn.rb}
# server 127.0.0.1:8080;
}
## This is a normal HTTP host which redirects all traffic to the HTTPS host.
server {
listen *:80;
## Replace git.example.com with your FQDN.
server_name git.example.com;
server_tokens off;
## This doesn't have to be a valid path since we are redirecting,
## you don't have to change it.
root /nowhere;
rewrite ^ https://$server_name$request_uri permanent;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
## Replace git.example.com with your FQDN.
server_name git.example.com;
server_tokens off;
root /home/git/gitlab/public;
## Increase this if you want to upload large attachments
## Or if you want to accept large git objects over http
client_max_body_size 20m;
## Strong SSL Security
## https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Strong_SSL_Security_On_nginx.html
ssl on;
ssl_certificate /usr/local/nginx/ssl/gitlab.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/nginx/ssl/gitlab.key;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_session_cache builtin:1000 shared:SSL:10m;
#add_header Strict-Transport-Security max-age=63072000;
#add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
#add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
## Individual nginx logs for this GitLab vhost
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/gitlab_access.log;
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/gitlab_error.log;
location / {
## Serve static files from defined root folder.
## @gitlab is a named location for the upstream fallback, see below.
try_files $uri $uri/index.html $uri.html @gitlab;
}
## If a file, which is not found in the root folder is requested,
## then the proxy pass the request to the upsteam (gitlab unicorn).
location @gitlab {
## If you use https make sure you disable gzip compression
## to be safe against BREACH attack.
gzip off;
## https://github.com/gitlabhq/gitlabhq/issues/694
## Some requests take more than 30 seconds.
proxy_read_timeout 300;
proxy_connect_timeout 300;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Ssl on;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
}
## Enable gzip compression as per rails guide:
## http://guides.rubyonrails.org/asset_pipeline.html#gzip-compression
#location ~ ^/(assets)/ {
# root /home/git/gitlab/public;
# gzip_static on; # to serve pre-gzipped version
# expires max;
# add_header Cache-Control public;
#}
error_page 502 /502.html;
}
————————————————————————————————————
2.将nginx加入git用户组(重要)
# usermod -a -G git nginx
# chmod g+rx /home/git/
3.生成ssl证书
# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/ssl
# cd /usr/local/nginx/ssl
# openssl req -new -x509 -nodes -days 3560 -out gitlab.crt -keyout gitlab.key
4.启动nginx
# service nginx start
5.打开web页面 git.example.com
nginx直接跳转URL为https://git.example.com
注:视浏览器不同这里首先会提示证书不受信任,因为我们在此是自己给自己颁发的证书,所以非官方CA授权,有需要授权的朋友可以通过很多其他途径购买.
GitLab默认的账号密码如下:
admin@local.host/5iveL!fe
Client端配置:
六.上传git仓库
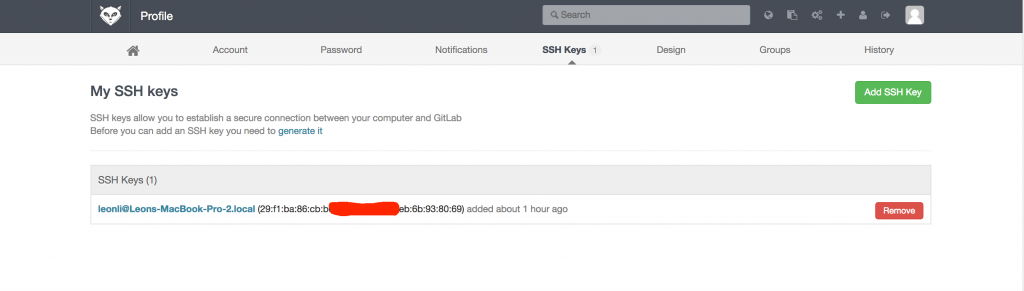
1.客户端生成秘钥
# cd ~
# ssh-keygen -t rsa
一路回车后生成公钥和秘钥对
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
—————————————————————————————————————————————————
将这里生成的秘钥全部复制并粘贴到gitlab web SSH Keys后台保存即可
—————————————————————————————————————————————————
上传后如图:
2.测试SSH连接
# ssh -p22 git@git.example.com
若报如下错误:
——————————————————————————————————————
PTY allocation request failed on channel 1
/usr/bin/env: ruby: No such file or directory
Connection to git.example.com closed.
——————————————————————————————————————
说明服务端ruby环境变量未在此目录/usr/bin/ruby
在服务器端加此软链即可:
# ln -s /usr/local/ruby/bin/ruby /usr/bin/ruby
注:若服务器端SSH自定义端口,则需要在客户端~/.ssh/config下添加端口配置
假定自定义SSH端口为2222
# echo “Port 2222” >> ~/.ssh/config
3.重新连接
# ssh -p22 git@git.example.com
——————————————————————————————————————
PTY allocation request failed on channel 1
Welcome to GitLab, Anonymous!
Connection to git.example.com closed.
——————————————————————————————————————
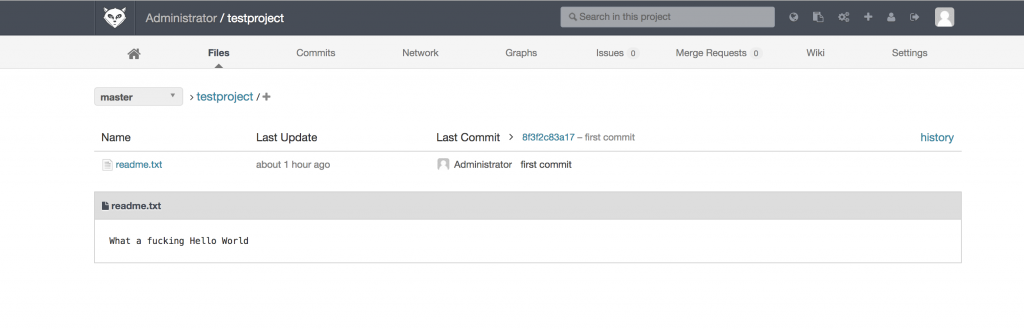
4.命令行上传git仓库
# su -
# mkdir testprojiect
# cd testprojiect/
# git init
# echo "What a fucking Hello World" > readme.txt
# git add .
# git commit -m 'first commit'
# git remote add origin git@git.example.com:root/testproject.git
# git push -u origin master
————————————————————————————————————————————
Counting objects: 3, done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 238 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To git@git.example.com:root/testproject.git
* [new branch] master -> master
Branch master set up to track remote branch master from origin.
————————————————————————————————————————————
大功告成...