Masonry介绍与使用实践:快速上手Autolayout
前言
MagicNumber -> autoresizingMask -> autolayout
以上是纯手写代码所经历的关于页面布局的三个时期
- 在iphone1-iphone3gs时代 window的size固定为(320,480) 我们只需要简单计算一下相对位置就好了
-
在iphone4-iphone4s时代 苹果推出了retina屏 但是给了码农们非常大的福利:window的size不变
-
在iphone5-iphone5s时代 window的size变了(320,568) 这时autoresizingMask派上了用场(为啥这时候不用Autolayout? 因为还要支持ios5呗) 简单的适配一下即可
在iphone6+时代 window的width也发生了变化(相对5和5s的屏幕比例没有变化) 终于是时候抛弃autoresizingMask改用autolayout了(不用支持ios5了 相对于屏幕适配的多样性来说autoresizingMask也已经过时了)
那如何快速的上手autolayout呢? 说实话 当年ios6推出的同时新增了autolayout的特性 我看了一下官方文档和demo 就立马抛弃到一边了 因为实在过于的繁琐和啰嗦(有过经验的朋友肯定有同感)
直到iphone6发布之后 我知道使用autolayout势在必行了 这时想起了以前在浏览Github看到过的一个第三方库Masonry 在花了几个小时的研究使用后 我就将autolayout掌握了(重点是我并没有学习任何的官方文档或者其他的关于autolayout的知识) 这就是我为什么要写下这篇文章来推荐它的原因
介绍
Masonry是一个轻量级的布局框架 拥有自己的描述语法 采用更优雅的链式语法封装自动布局 简洁明了 并具有高可读性 而且同时支持 iOS 和 Max OS X
我们先来看一段官方的sample code来认识一下Masonry
[view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(superview).with.insets(padding);
}];
看到block里面的那句话: make edges equalTo superview with insets
通过链式的自然语言 就把view1给autolayout好了 是不是简单易懂?
使用
看一下Masonry支持哪一些属性
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *left;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *top;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *right;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *bottom;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *leading;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *trailing;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *width;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *height;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *centerX;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *centerY;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *baseline;
这些属性与NSLayoutAttrubute的对照表如下
| Masonry | NSAutoLayout | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| left | NSLayoutAttributeLeft | 左侧 |
| top | NSLayoutAttributeTop | 上侧 |
| right | NSLayoutAttributeRight | 右侧 |
| bottom | NSLayoutAttributeBottom | 下侧 |
| leading | NSLayoutAttributeLeading | 首部 |
| trailing | NSLayoutAttributeTrailing | 尾部 |
| width | NSLayoutAttributeWidth | 宽 |
| height | NSLayoutAttributeHeight | 高 |
| centerX | NSLayoutAttributeCenterX | 横向中点 |
| centerY | NSLayoutAttributeCenterY | 纵向中点 |
| baseline | NSLayoutAttributeBaseline | 文本基线 |
其中leading与left trailing与right 在正常情况下是等价的 但是当一些布局是从右至左时(比如阿拉伯文?没有类似的经验) 则会对调 换句话说就是基本可以不理不用 用left和right就好了
在ios8发布后 又新增了一堆奇奇怪怪的属性(有兴趣的朋友可以去瞅瞅) Masonry暂时还不支持(不过你要支持ios6,ios7 就没必要去管那么多了)
下面进入正题(为了方便 我们测试的superView都是一个size为(300,300)的UIView)
下面 通过一些简单的实例来简单介绍如何轻松愉快的使用Masonry:
[基础] 居中显示一个view
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
UIView *sv = [UIView new];
[sv showPlaceHolder];
sv.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
[self.view addSubview:sv];
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.center.equalTo(self.view);
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));
}];
}
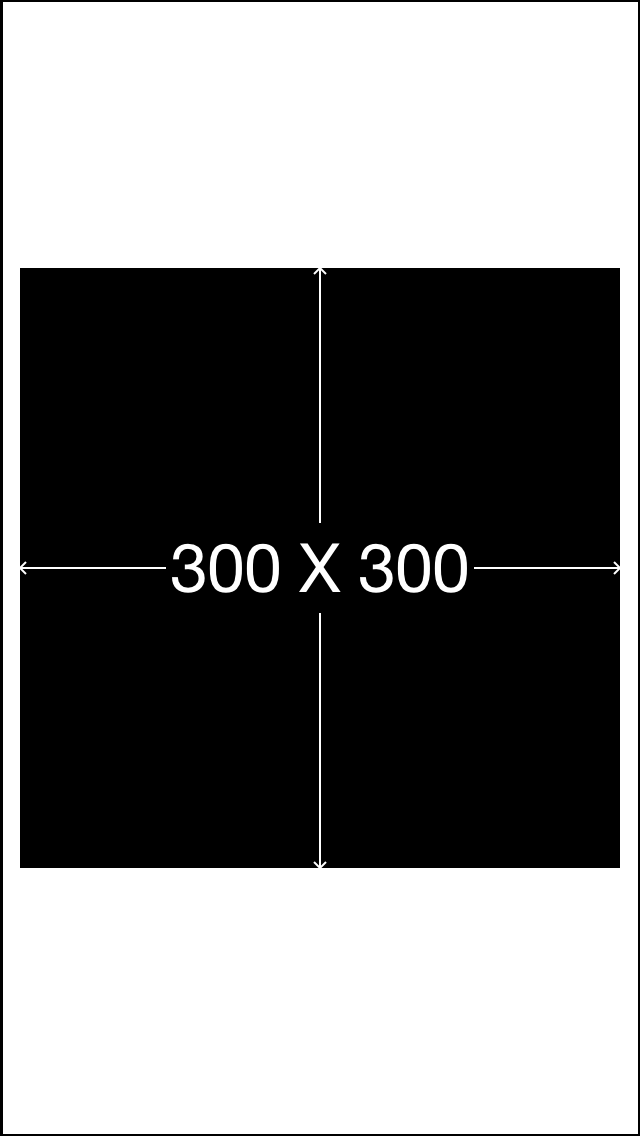
使用我之间写的MMPlaceHolder 可以看到superview已经按照我们预期居中并且设置成了适当的大小
那么先看看这几行代码
//从此以后基本可以抛弃CGRectMake了
UIView *sv = [UIView new];
//在做autoLayout之前 一定要先将view添加到superview上 否则会报错
[self.view addSubview:sv];
//mas_makeConstraints就是Masonry的autolayout添加函数 将所需的约束添加到block中行了
[sv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
//将sv居中(很容易理解吧?)
make.center.equalTo(self.view);
//将size设置成(300,300)
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(300, 300));
}];
这里有两个问题要分解一下
- 首先在Masonry中能够添加autolayout约束有三个函数
- (NSArray *)mas_makeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block;
- (NSArray *)mas_updateConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block;
- (NSArray *)mas_remakeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block;
/*
mas_makeConstraints 只负责新增约束 Autolayout不能同时存在两条针对于同一对象的约束 否则会报错
mas_updateConstraints 针对上面的情况 会更新在block中出现的约束 不会导致出现两个相同约束的情况
mas_remakeConstraints 则会清除之前的所有约束 仅保留最新的约束
三种函数善加利用 就可以应对各种情况了
*/
- 其次 equalTo 和 mas_equalTo的区别在哪里呢? 其实 mas_equalTo是一个MACRO
#define mas_equalTo(...) equalTo(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#define mas_greaterThanOrEqualTo(...) greaterThanOrEqualTo(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#define mas_lessThanOrEqualTo(...) lessThanOrEqualTo(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#define mas_offset(...) valueOffset(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
可以看到 mas_equalTo只是对其参数进行了一个BOX操作(装箱) MASBoxValue的定义具体可以看看源代码 太长就不贴出来了
所支持的类型 除了NSNumber支持的那些数值类型之外 就只支持CGPoint CGSize UIEdgeInsets
介绍完这几个问题 我们就继续往下了 PS:刚才定义的sv会成为我们接下来所有sample的superView
[初级] 让一个view略小于其superView(边距为10)
UIView *sv1 = [UIView new];
[sv1 showPlaceHolder];
sv1.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
[sv addSubview:sv1];
[sv1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(sv).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10));
/* 等价于
make.top.equalTo(sv).with.offset(10);
make.left.equalTo(sv).with.offset(10);
make.bottom.equalTo(sv).with.offset(-10);
make.right.equalTo(sv).with.offset(-10);
*/
/* 也等价于
make.top.left.bottom.and.right.equalTo(sv).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10));
*/
}];
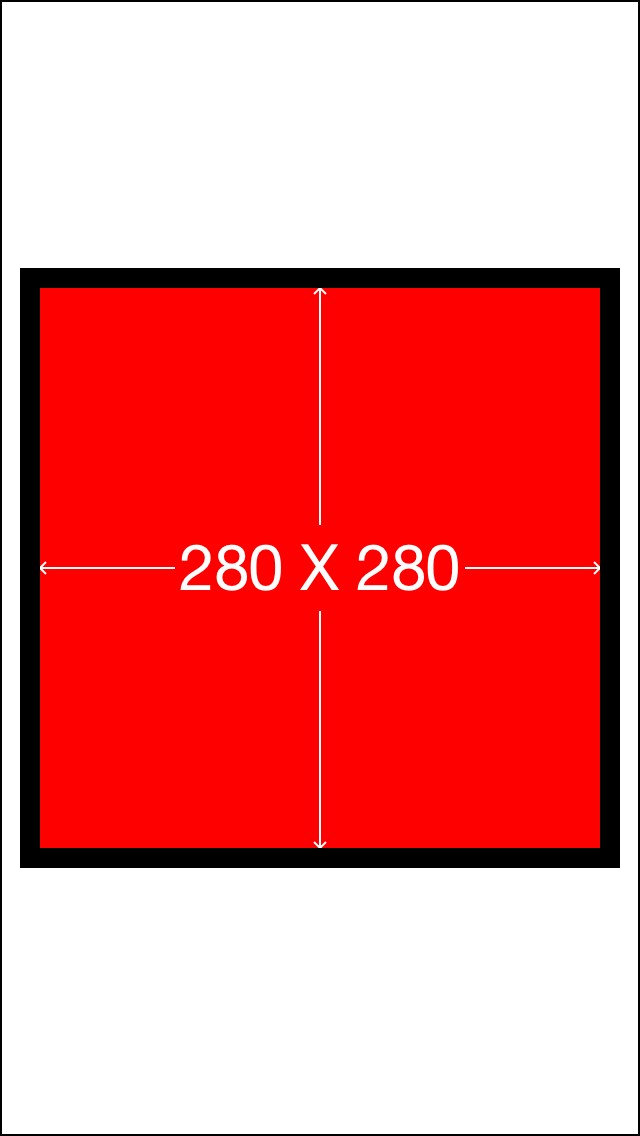
可以看到 edges 其实就是top,left,bottom,right的一个简化 分开写也可以 一句话更省事
那么为什么bottom和right里的offset是负数呢? 因为这里计算的是绝对的数值 计算的bottom需要小于sv的底部高度 所以要-10 同理用于right
这里有意思的地方是and和with 其实这两个函数什么事情都没做
- (MASConstraint *)with {
return self;
}
- (MASConstraint *)and {
return self;
}
但是用在这种链式语法中 就非常的巧妙和易懂 不得不佩服作者的心思(虽然我现在基本都会省略)
[初级] 让两个高度为150的view垂直居中且等宽且等间隔排列 间隔为10(自动计算其宽度)
int padding1 = 10;
[sv2 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.centerY.mas_equalTo(sv.mas_centerY);
make.left.equalTo(sv.mas_left).with.offset(padding1);
make.right.equalTo(sv3.mas_left).with.offset(-padding1);
make.height.mas_equalTo(@150);
make.width.equalTo(sv3);
}];
[sv3 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.centerY.mas_equalTo(sv.mas_centerY);
make.left.equalTo(sv2.mas_right).with.offset(padding1);
make.right.equalTo(sv.mas_right).with.offset(-padding1);
make.height.mas_equalTo(@150);
make.width.equalTo(sv2);
}];
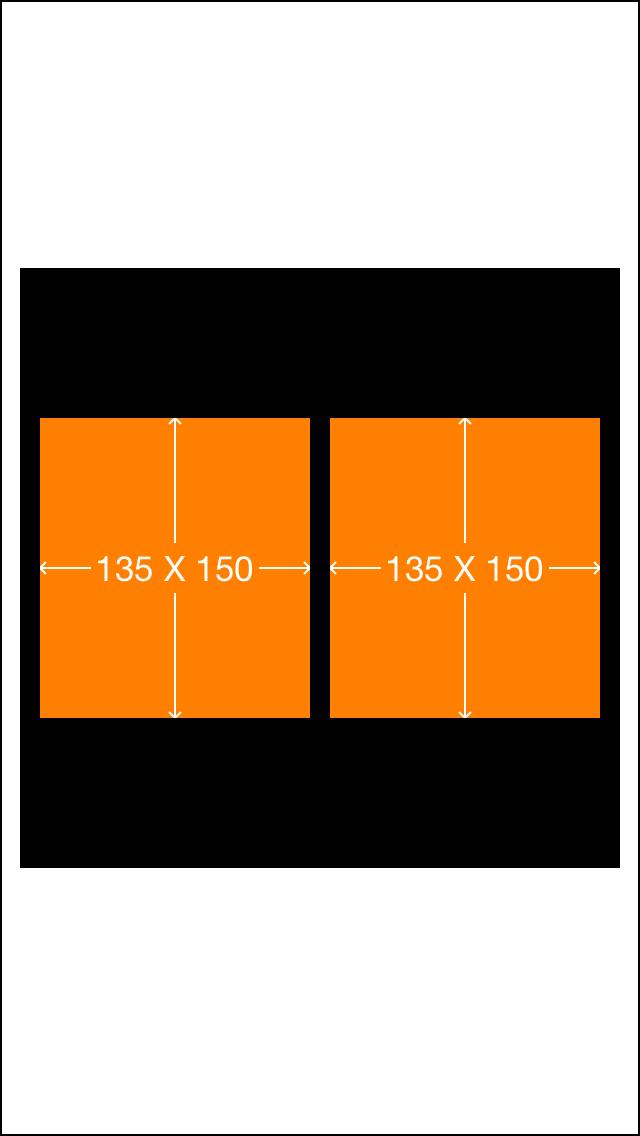
这里我们在两个子view之间互相设置的约束 可以看到他们的宽度在约束下自动的被计算出来了
[中级] 在UIScrollView顺序排列一些view并自动计算contentSize
UIScrollView *scrollView = [UIScrollView new];
scrollView.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[sv addSubview:scrollView];
[scrollView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(sv).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(5,5,5,5));
}];
UIView *container = [UIView new];
[scrollView addSubview:container];
[container mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.equalTo(scrollView);
make.width.equalTo(scrollView);
}];
int count = 10;
UIView *lastView = nil;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= count ; ++i )
{
UIView *subv = [UIView new];
[container addSubview:subv];
subv.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithHue:( arc4random() % 256 / 256.0 )
saturation:( arc4random() % 128 / 256.0 ) + 0.5
brightness:( arc4random() % 128 / 256.0 ) + 0.5
alpha:1];
[subv mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.left.and.right.equalTo(container);
make.height.mas_equalTo(@(20*i));
if ( lastView )
{
make.top.mas_equalTo(lastView.mas_bottom);
}
else
{
make.top.mas_equalTo(container.mas_top);
}
}];
lastView = subv;
}
[container mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.bottom.equalTo(lastView.mas_bottom);
}];
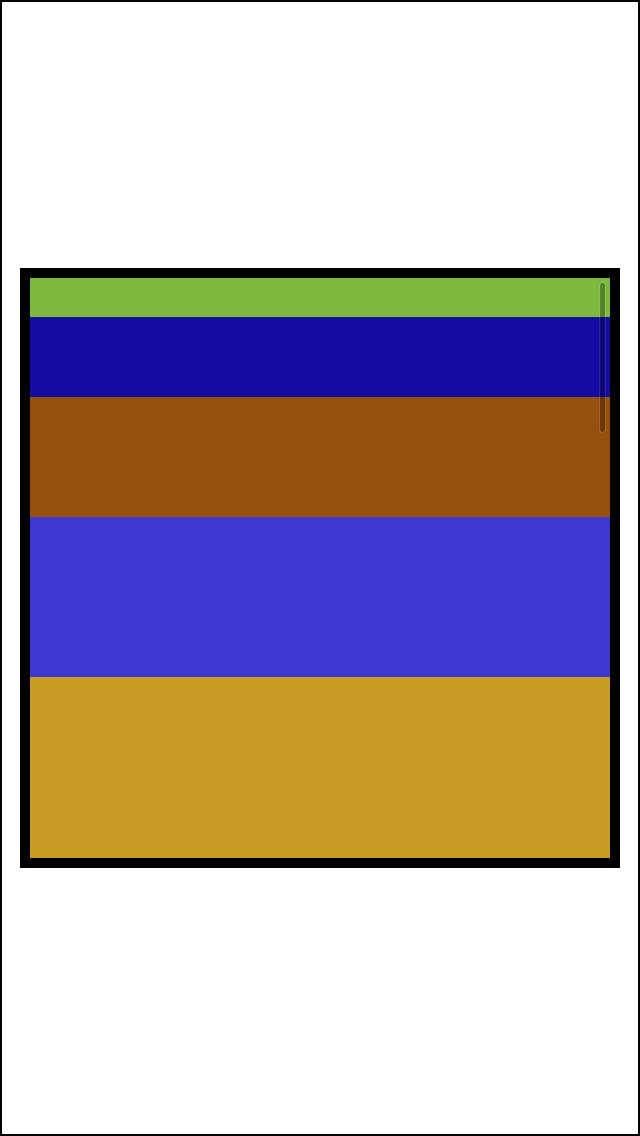
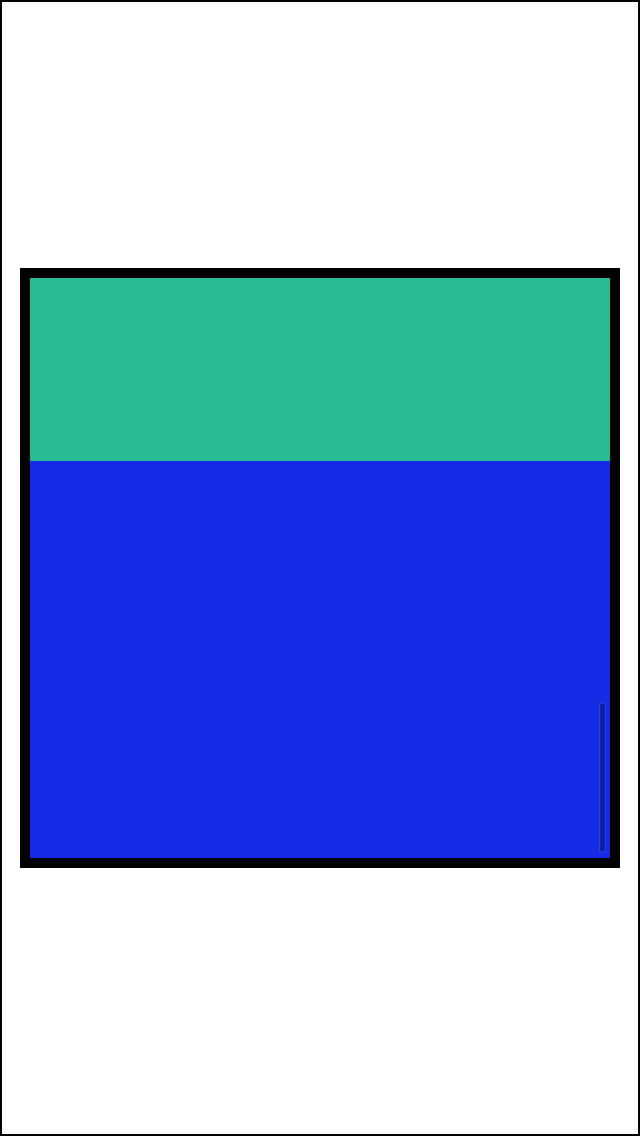
从scrollView的scrollIndicator可以看出 scrollView的内部已如我们所想排列好了
这里的关键就在于container这个view起到了一个中间层的作用 能够自动的计算uiscrollView的contentSize
[高级] 横向或者纵向等间隙的排列一组view
很遗憾 autoLayout并没有直接提供等间隙排列的方法(Masonry的官方demo中也没有对应的案例) 但是参考案例3 我们可以通过一个小技巧来实现这个目的 为此我写了一个Category
@implementation UIView(Masonry_LJC)
- (void) distributeSpacingHorizontallyWith:(NSArray*)views
{
NSMutableArray *spaces = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:views.count+1];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < views.count+1 ; ++i )
{
UIView *v = [UIView new];
[spaces addObject:v];
[self addSubview:v];
[v mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.width.equalTo(v.mas_height);
}];
}
UIView *v0 = spaces[0];
[v0 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.left.equalTo(self.mas_left);
make.centerY.equalTo(((UIView*)views[0]).mas_centerY);
}];
UIView *lastSpace = v0;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < views.count; ++i )
{
UIView *obj = views[i];
UIView *space = spaces[i+1];
[obj mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.left.equalTo(lastSpace.mas_right);
}];
[space mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.left.equalTo(obj.mas_right);
make.centerY.equalTo(obj.mas_centerY);
make.width.equalTo(v0);
}];
lastSpace = space;
}
[lastSpace mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.right.equalTo(self.mas_right);
}];
}
- (void) distributeSpacingVerticallyWith:(NSArray*)views
{
NSMutableArray *spaces = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:views.count+1];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < views.count+1 ; ++i )
{
UIView *v = [UIView new];
[spaces addObject:v];
[self addSubview:v];
[v mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.width.equalTo(v.mas_height);
}];
}
UIView *v0 = spaces[0];
[v0 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(self.mas_top);
make.centerX.equalTo(((UIView*)views[0]).mas_centerX);
}];
UIView *lastSpace = v0;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < views.count; ++i )
{
UIView *obj = views[i];
UIView *space = spaces[i+1];
[obj mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(lastSpace.mas_bottom);
}];
[space mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(obj.mas_bottom);
make.centerX.equalTo(obj.mas_centerX);
make.height.equalTo(v0);
}];
lastSpace = space;
}
[lastSpace mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.bottom.equalTo(self.mas_bottom);
}];
}
@end
简单的来测试一下
UIView *sv11 = [UIView new];
UIView *sv12 = [UIView new];
UIView *sv13 = [UIView new];
UIView *sv21 = [UIView new];
UIView *sv31 = [UIView new];
sv11.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
sv12.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
sv13.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
sv21.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
sv31.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
[sv addSubview:sv11];
[sv addSubview:sv12];
[sv addSubview:sv13];
[sv addSubview:sv21];
[sv addSubview:sv31];
//给予不同的大小 测试效果
[sv11 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.centerY.equalTo(@[sv12,sv13]);
make.centerX.equalTo(@[sv21,sv31]);
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(40, 40));
}];
[sv12 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(70, 20));
}];
[sv13 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(50, 50));
}];
[sv21 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(50, 20));
}];
[sv31 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(40, 60));
}];
[sv distributeSpacingHorizontallyWith:@[sv11,sv12,sv13]];
[sv distributeSpacingVerticallyWith:@[sv11,sv21,sv31]];
[sv showPlaceHolderWithAllSubviews];
[sv hidePlaceHolder];
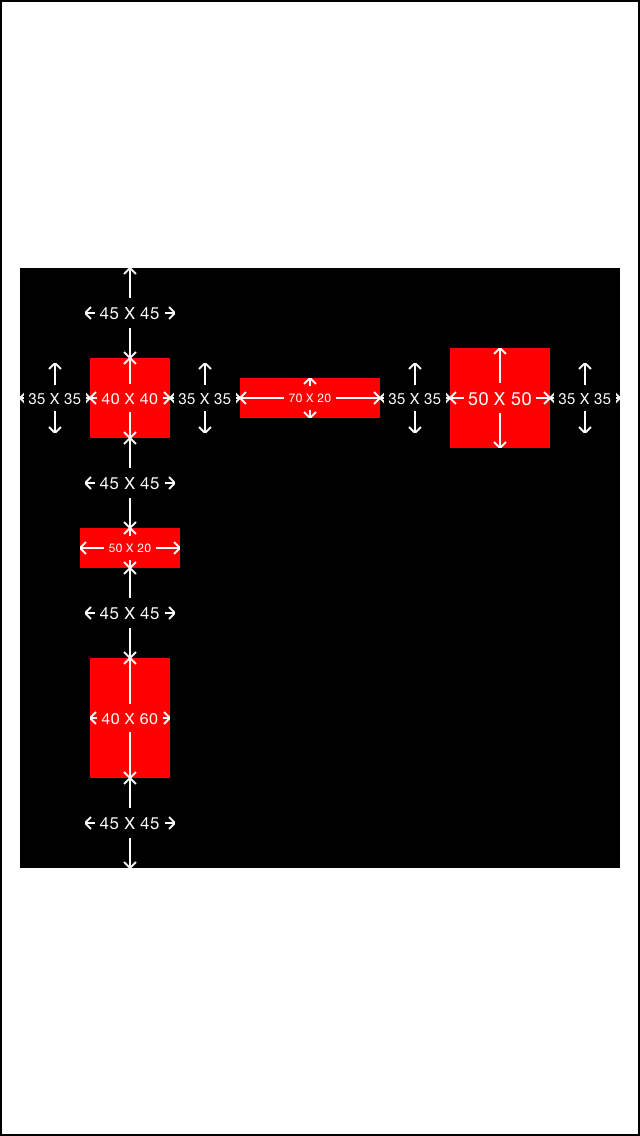
perfect! 简洁明了的达到了我们所要的效果
这里所用的技巧就是 使用空白的占位view来填充我们目标view的旁边 这点通过图上的空白标注可以看出来
小结
通过以上5个案例 我觉得已经把Masonry的常用功能介绍得差不多了 以上五个例子的代码可以在这里找到 如果你觉得意犹未尽呢 请下载官方的demo来学习
总而言之 Masonry是一个非常优秀的autolayout库 能够节省大量的开发和学习时间 尤其适合我这种纯代码的iOSer 在iPhone6发布后引发的适配潮中 Masonry一定可以助你一臂之力 