继前文Flink 原理与实现:架构和拓扑概览中介绍了Flink的四层执行图模型,本文将主要介绍 Flink 是如何将 StreamGraph 转换成 JobGraph 的。根据用户用Stream API编写的程序,构造出一个代表拓扑结构的StreamGraph的。以 WordCount 为例,转换图如下图所示:
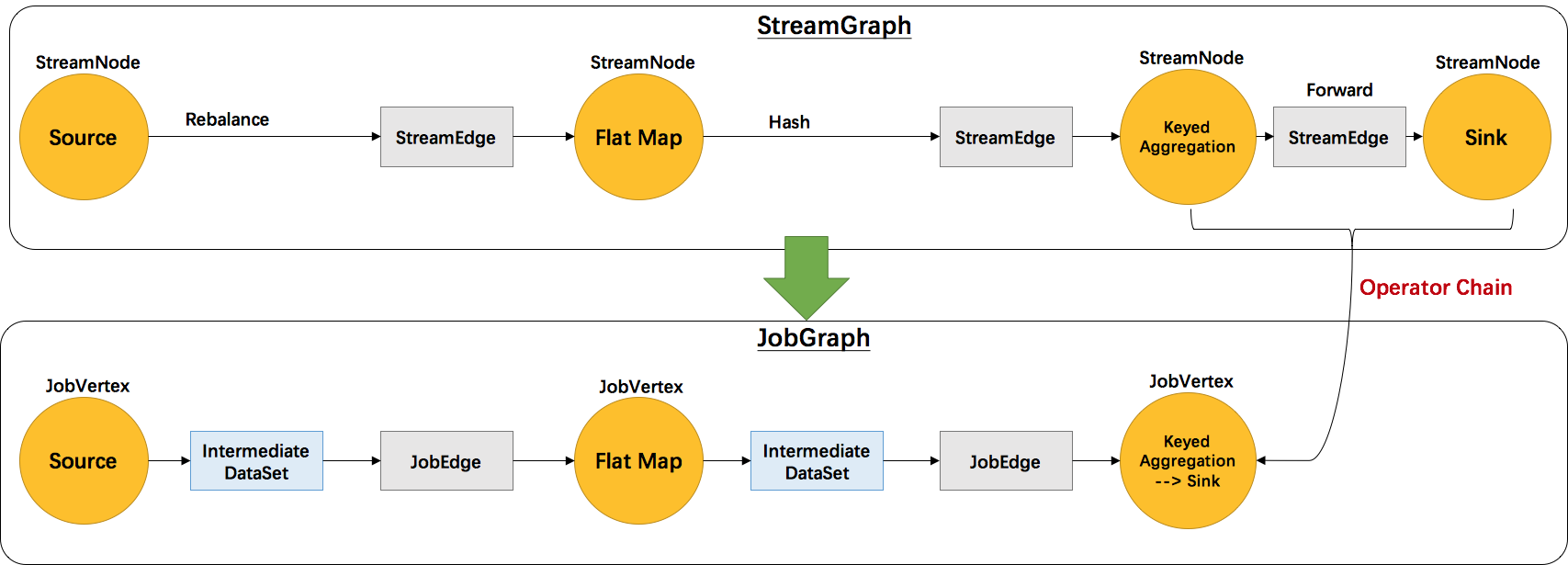
StreamGraph 和 JobGraph 都是在 Client 端生成的,也就是说我们可以在 IDE 中通过断点调试观察 StreamGraph 和 JobGraph 的生成过程。
JobGraph 的相关数据结构主要在 org.apache.flink.runtime.jobgraph 包中。构造 JobGraph 的代码主要集中在 StreamingJobGraphGenerator 类中,入口函数是 StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph()。我们首先来看下StreamingJobGraphGenerator的核心源码:
public class StreamingJobGraphGenerator {
private StreamGraph streamGraph;
private JobGraph jobGraph;
private Map<Integer, JobVertex> jobVertices;
private Collection<Integer> builtVertices;
private List<StreamEdge> physicalEdgesInOrder;
private Map<Integer, Map<Integer, StreamConfig>> chainedConfigs;
private Map<Integer, StreamConfig> vertexConfigs;
private Map<Integer, String> chainedNames;
public StreamingJobGraphGenerator(StreamGraph streamGraph) {
this.streamGraph = streamGraph;
}
public JobGraph createJobGraph() {
jobGraph = new JobGraph(streamGraph.getJobName());
jobGraph.setScheduleMode(ScheduleMode.ALL);
init();
Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes = traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes();
setChaining(hashes);
setPhysicalEdges();
setSlotSharing();
configureCheckpointing();
configureRestartStrategy();
try {
InstantiationUtil.writeObjectToConfig(this.streamGraph.getExecutionConfig(), this.jobGraph.getJobConfiguration(), ExecutionConfig.CONFIG_KEY);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Config object could not be written to Job Configuration: ", e);
}
return jobGraph;
}
...
}
|
StreamingJobGraphGenerator的成员变量都是为了辅助生成最终的JobGraph。createJobGraph()函数的逻辑也很清晰,首先为所有节点生成一个唯一的hash id,这个id不会因多次提交而改变,这主要用于故障恢复。这里我们不能用 StreamNode.id来代替,因为这是一个从1开始的静态计数变量,同一个Job的多次提交可能会得到不一样的id。然后就是最关键的chaining处理,和生成JobVetex、JobEdge等。之后就是写入各种配置相关的信息。
下面具体分析下关键函数 setChaining 的实现:
private void setChaining(Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes) {
for (Integer sourceNodeId : streamGraph.getSourceIDs()) {
createChain(sourceNodeId, sourceNodeId, hashes);
}
}
private List<StreamEdge> createChain(
Integer startNodeId,
Integer currentNodeId,
Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes) {
if (!builtVertices.contains(startNodeId)) {
List<StreamEdge> transitiveOutEdges = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
List<StreamEdge> chainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
List<StreamEdge> nonChainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
for (StreamEdge outEdge : streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOutEdges()) {
if (isChainable(outEdge)) {
chainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
} else {
nonChainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
}
}
for (StreamEdge chainable : chainableOutputs) {
transitiveOutEdges.addAll(createChain(startNodeId, chainable.getTargetId(), hashes));
}
for (StreamEdge nonChainable : nonChainableOutputs) {
transitiveOutEdges.add(nonChainable);
createChain(nonChainable.getTargetId(), nonChainable.getTargetId(), hashes);
}
chainedNames.put(currentNodeId, createChainedName(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
StreamConfig config = currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)
? createJobVertex(startNodeId, hashes)
: new StreamConfig(new Configuration());
setVertexConfig(currentNodeId, config, chainableOutputs, nonChainableOutputs);
if (currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)) {
config.setChainStart();
config.setOutEdgesInOrder(transitiveOutEdges);
config.setOutEdges(streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOutEdges());
for (StreamEdge edge : transitiveOutEdges) {
connect(startNodeId, edge);
}
config.setTransitiveChainedTaskConfigs(chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId));
} else {
Map<Integer, StreamConfig> chainedConfs = chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId);
if (chainedConfs == null) {
chainedConfigs.put(startNodeId, new HashMap<Integer, StreamConfig>());
}
chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId).put(currentNodeId, config);
}
return transitiveOutEdges;
} else {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}
|
每个 JobVertex 都会对应一个可序列化的 StreamConfig, 用来发送给 JobManager 和 TaskManager。最后在 TaskManager 中起 Task 时,需要从这里面反序列化出所需要的配置信息, 其中就包括了含有用户代码的StreamOperator。
setChaining会对source调用createChain方法,该方法会递归调用下游节点,从而构建出node chains。createChain会分析当前节点的出边,根据Operator Chains中的chainable条件,将出边分成chainalbe和noChainable两类,并分别递归调用自身方法。之后会将StreamNode中的配置信息序列化到StreamConfig中。如果当前不是chain中的子节点,则会构建 JobVertex 和 JobEdge相连。如果是chain中的子节点,则会将StreamConfig添加到该chain的config集合中。一个node chains,除了 headOfChain node会生成对应的 JobVertex,其余的nodes都是以序列化的形式写入到StreamConfig中,并保存到headOfChain的 CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG 配置项中。直到部署时,才会取出并生成对应的ChainOperators,具体过程请见理解 Operator Chains。
总结
本文主要对 Flink 中将 StreamGraph 转变成 JobGraph 的核心源码进行了分析。思想还是很简单的,StreamNode 转成 JobVertex,StreamEdge 转成 JobEdge,JobEdge 和 JobVertex 之间创建 IntermediateDataSet 来连接。关键点在于将多个 SteamNode chain 成一个 JobVertex的过程,这部分源码比较绕,有兴趣的同学可以结合源码单步调试分析。下一章将会介绍 JobGraph 提交到 JobManager 后是如何转换成分布式化的 ExecutionGraph 的。
