Mac+Docker+Ansible部署WordPress Application
很久没有更新博客了,今天给大家在这里推荐使用Docker部署Wordpress Application
Docker就不多介绍了,大家可以理解为是他是一个虚拟集装箱,将原来以服务器为基础单元的集群,细化到以每个服务进程为单元。这样的优点在于:
1. 隔离开发环境和具体可执行进程,可跨平台及夸主机使用
2. 节约时间成本,硬件成本,秒级别快速部署启动
3. 支持持续集成,可利用相关部署工具(Ansible, saltstack)进行快速部署
4. 可作为轻量级别主机或节点部署应用
5. 未来可能代替虚拟机的虚拟容器
然后利用Ansible去对Docker容器进行具体服务的部署,最大限度的体现轻量级,节约硬件成本的好处。
在部署之前首先给大家介绍一下我的部署结构:
dockerfiles
├── mariadb
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ ├── ansible
│ │ ├── mariadb-install-container.yml
│ │ ├── mariadb.sh
│ │ ├── mariadb.sql
│ │ └── my.cnf
│ └── run.sh
├── nginx
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ ├── ansible
│ │ ├── default.conf
│ │ ├── nginx-container.yml
│ │ └── nginx.conf
│ └── run.sh
└── php
├── Dockerfile
├── ansible
│ ├── info.php
│ ├── php-container.yml
│ ├── test-db-conn.php
│ ├── wp-config.php
│ └── http://www.conf
└── run.sh
Dockerfiles主目录下面分别是3个服务所对应的目录,每个目录大致分为Dockerfile配置文件, ansible目录,以及run.sh
Dockerfile这个大家都清楚,用来Build容器镜像的配置脚本。
ansible目录下保存需要在容器内使用到的ansible playbook相应配置文件。
run.sh则是创建和运行容器的启动脚本,我们分别去执行对应目录的执行脚本用来构建Docker容器所对应的服务。
这里给大家提供一个我的gitlab私人仓库的链接,方便大家去下载这个部署脚本:
https://git.yanwenbo.cn/showerlee/ansible-docker-wp
大家如果想对Docker和Ansible有不太明白的地方可以先阅读我之前写的文章。
Docker: http://www.showerlee.com/archives/1758
Ansible: http://www.showerlee.com/archives/1649
一.环境部署
Local system: MAC OS X 10.12.1
Docker: Docker 1.12.3
Tip: 这里说明一下,较早版本的Docker若在非Linux内核下去安装需要去配合安装virtualbox虚拟机才能正常使用,这里我们使用的官方最新版本的Docker目前已经解决了这个问题,他会使用MAC内核去直接创建Docker虚拟容器,不需要依赖其他的工具。
二.Docker部署
Mariadb container
Mariadb是Mysql在CentOS7上的一个开源分支, 大家可以理解就是一个mysql. 这里首先我们为什么先去部署并启动Mariadb, 是因为我们后面启动Docker时会用到它的一个Link参数,这个参数不仅保证两台容器会安全的利用这个Link去传输数据,而且还会在被Link主机内创建一个host记录,方便我们直接用FQDN名去访问相应主机。
Dockerfile
FROM ansible/centos7-ansible/:stable ADD ansible /data/ansible WORKDIR /data/ansible RUN ansible-playbook mariadb-install-container.yml -c local # Initialize and start mariadb RUN chmod +x mariadb.sh CMD ["./mariadb.sh"] EXPOSE 3306
这里简单来说就是下载集成Ansible的CentOS7容器镜像,并将ansible playbook及相应配置文件复制到容器内去部署MariaDB初始环境,最终启动服务,并开启3306DB端口.
ansible/mariadb-install-container.yml
- name: Install Mariadb container
hosts: local
vars:
conf_path: /etc/my.cnf
src_socket: /data/mariadb_data/mysql.sock
link_socket: /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
user: mysql
tasks:
- name: Install epel-release package
yum: name=epel-release state=latest
- name: Install required packages
yum: name={{ item }} state=latest
with_items:
- net-tools
- lsof
- nmap
- mariadb-server
- MySQL-python
- name: Copy mariadb conf
copy: src=my.cnf dest={{ conf_path }} mode=0644
- name: Link mysql socket
file:
src={{ src_socket }} dest={{ link_socket }} state=link force=yes
这里是ansible playbook, 基本上就是利用ansible本地安装Epel源以及Mariadb相应的安装包,然后进行DB的相关配置。
ansible/mariadb.sh
#!/bin/sh
chown -R mysql:mysql /var/lib/mysql
mysql_install_db --user=mysql --datadir=/data/mariadb_data > /dev/null
mysqld_safe &
sleep 5s
mysql -v < mariadb.sql
sleep 5s
ps -wef | grep mysql | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9
mysqld_safe --user mysql
这里是对Mariadb进行初始化安装,并使用sql脚本更改root密码及相应权限和创建Wordpress数据库,最终重启DB服务。
ansible/Mariadb.sql
USE mysql;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
UPDATE user SET password=PASSWORD("123456") WHERE user='root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
CREATE DATABASE wordpress;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
ansible/my.cnf
[mysqld] datadir=/data/mariadb_data socket=/data/mariadb_data/mysql.sock port=3306 bind-address = 0.0.0.0 # Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks symbolic-links=0 # Settings user and group are ignored when systemd is used. # If you need to run mysqld under a different user or group, # customize your systemd unit file for mariadb according to the # instructions in http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Systemd [mysqld_safe] log-error=/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log pid-file=/var/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid # # include all files from the config directory # !includedir /etc/my.cnf.d
Mariadb的DB配置.
run.sh
#/bin/bash
IMAGE="leon/mariadb"
Container="mariadb"
docker build -t ${IMAGE} .
docker run -d -p 3306:3306 --name ${Container} ${IMAGE}
最终我们使用docker build去创建一个基于Dockerfile配置的MariaDB容器镜像,并用docker run去启动这个容器镜像。
Tip: -d为后台启动容器,-p为打开端口,--name 为创建容器名,-t为打一个镜像标签。
PHP container
接下来我们会部署启动php-fpm服务,作为解析Wordpress网站的php服务, 它会开启9000端口,方便后面的nginx container去进行反向连接。
Dockerfile
FROM ansible/centos7-ansible:stable ADD ansible /data/ansible WORKDIR /data/ansible RUN ansible-playbook php-container.yml -c local # Add the volume to php application VOLUME ["/data/app"] # CMD ["php-fpm", "--nodaemonize"] ENTRYPOINT ["/usr/sbin/php-fpm", "-F"] EXPOSE 9000
这里的配置基本上和MariaDB类似,区别在于我们会在这里去创建一个与nginx共同使用的共享网站目录,里面会保存Wordpress源代码和相关php测试文件。
ansible/php-container.yml
- name: Create PHP container
hosts: local
vars:
app_dir: /data/app
src_dir: /data/src
phpfpm_path: /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
info_path: /data/app/info.php
test_path: /data/app/test-db-conn.php
wp_url: https://cn.wordpress.org/wordpress-4.5.3-zh_CN.tar.gz
wp_config: /data/app/wp-config.php
tasks:
- name: Install epel-release packages
yum: name=epel-release state=latest
- name: Install required packages
yum: name={{ item }} state=latest
with_items:
- net-tools
- lsof
- nmap
- unzip
- mariadb
- name: Install php packages
yum: name={{ item }} state=latest
with_items:
- php
- php-mysql
- php-fpm
- php-gd
- php-mbstring
- name: Create dir
file: path={{ item }} state=directory mode=0755
with_items:
- "{{ app_dir }}"
- "{{ src_dir }}"
- name: Unpack WP package
unarchive: src={{ wp_url }} dest={{ src_dir }} remote_src=yes
- name: Move WP source code to app_dir
shell: "shopt -s dotglob && mv {{ src_dir }}/wordpress/* {{ app_dir }}"
- name: Copy wp configuration
copy: src=wp-config.php dest={{ wp_config }}
- name: Copy php info page
copy: src=info.php dest={{ info_path }} mode=0755
- name: Copy test-db-conn page
copy: src=test-db-conn.php dest={{ test_path }} mode=0755
- name: Copy nginx configuration
copy: src=www.conf dest={{ phpfpm_path }} mode=0755
这里playbook配置内容较多,不过基本上就是安装php-fpm以及相应安装包,配置php-fpm配置项,并下载Wordpress源代码并将DB信息写入WP配置文件,复制php测试脚本等。
ansible/info.php
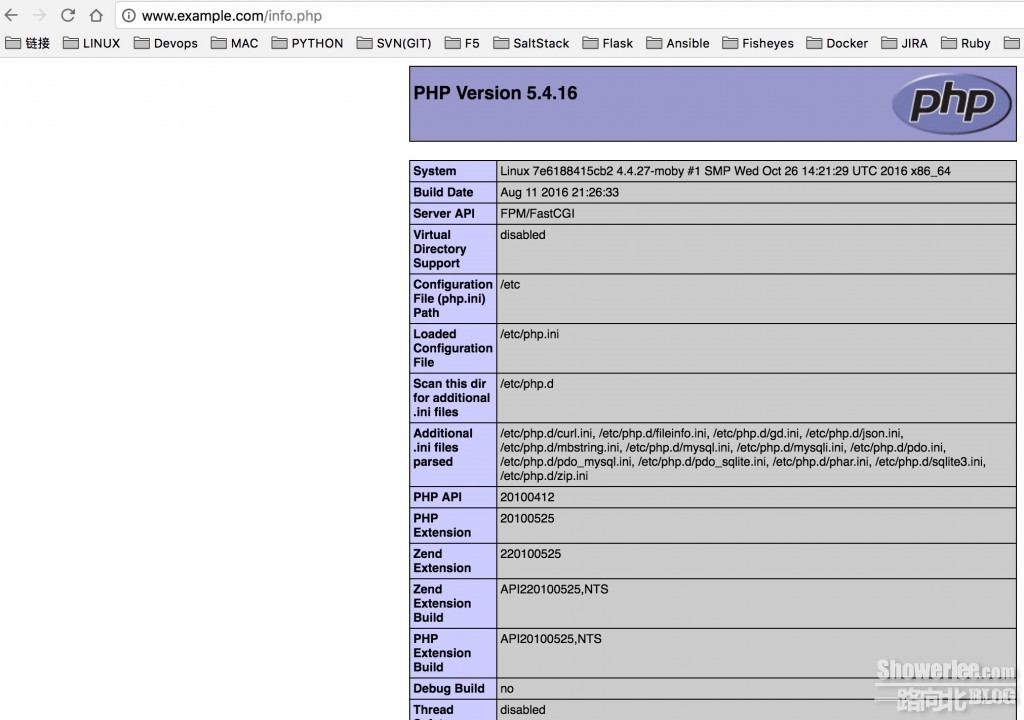
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
ansible/test-db-conn.php
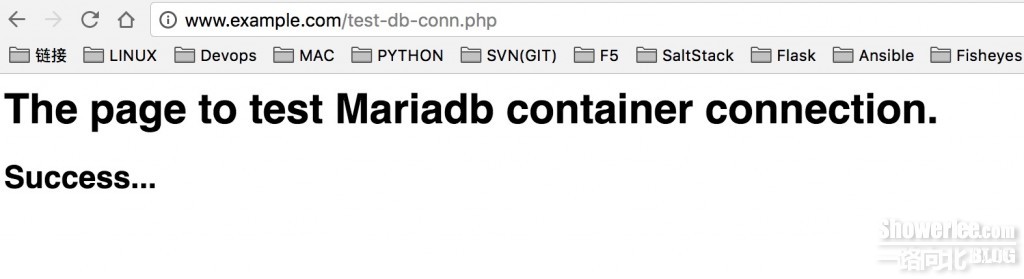
<html><body><h1>The page to test Mariadb connection.</h1></body></html>
<?php
$conn=mysql_connect('mariadb','root','123456');
if ($conn)
echo "<h2>Success...</h2>";
else
echo "<h2>Failure...</h2>";
?>
ansible/wp-config.php
<?php /** * WordPress基础配置文件。 * * 这个文件被安装程序用于自动生成wp-config.php配置文件, * 您可以不使用网站,您需要手动复制这个文件, * 并重命名为“wp-config.php”,然后填入相关信息。 * * 本文件包含以下配置选项: * * * MySQL设置 * * 密钥 * * 数据库表名前缀 * * ABSPATH * * @link https://codex.wordpress.org/zh-cn:%E7%BC%96%E8%BE%91_wp-config.php * * @package WordPress */ // ** MySQL 设置 - 具体信息来自您正在使用的主机 ** // /** WordPress数据库的名称 */ define('DB_NAME', 'wordpress'); /** MySQL数据库用户名 */ define('DB_USER', 'root'); /** MySQL数据库密码 */ define('DB_PASSWORD', '123456'); /** MySQL主机 */ define('DB_HOST', 'mariadb'); /** 创建数据表时默认的文字编码 */ define('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8'); /** 数据库整理类型。如不确定请勿更改 */ define('DB_COLLATE', ''); /**#@+ * 身份认证密钥与盐。 * * 修改为任意独一无二的字串! * 或者直接访问{@link https://api.wordpress.org/secret-key/1.1/salt/ * WordPress.org密钥生成服务} * 任何修改都会导致所有cookies失效,所有用户将必须重新登录。 * * @since 2.6.0 */ define('AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here'); define('SECURE_AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here'); define('LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here'); define('NONCE_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here'); define('AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here'); define('SECURE_AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here'); define('LOGGED_IN_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here'); define('NONCE_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here'); /**#@-*/ /** * WordPress数据表前缀。 * * 如果您有在同一数据库内安装多个WordPress的需求,请为每个WordPress设置 * 不同的数据表前缀。前缀名只能为数字、字母加下划线。 */ $table_prefix = 'wp_'; /** * 开发者专用:WordPress调试模式。 * * 将这个值改为true,WordPress将显示所有用于开发的提示。 * 强烈建议插件开发者在开发环境中启用WP_DEBUG。 * * 要获取其他能用于调试的信息,请访问Codex。 * * @link https://codex.wordpress.org/Debugging_in_WordPress */ define('WP_DEBUG', false); /** * zh_CN本地化设置:启用ICP备案号显示 * * 可在设置→常规中修改。 * 如需禁用,请移除或注释掉本行。 */ define('WP_ZH_CN_ICP_NUM', true); /* 好了!请不要再继续编辑。请保存本文件。使用愉快! */ /** WordPress目录的绝对路径。 */ if ( !defined('ABSPATH') ) define('ABSPATH', dirname(__FILE__) . '/'); /** 设置WordPress变量和包含文件。 */ require_once(ABSPATH . 'wp-settings.php');
ansible/www.conf
; Start a new pool named 'www'. [www] ; The address on which to accept FastCGI requests. ; Valid syntaxes are: ; 'ip.add.re.ss:port' - to listen on a TCP socket to a specific address on ; a specific port; ; 'port' - to listen on a TCP socket to all addresses on a ; specific port; ; '/path/to/unix/socket' - to listen on a unix socket. ; Note: This value is mandatory. listen = 0.0.0.0:9000 ; Set listen(2) backlog. A value of '-1' means unlimited. ; Default Value: -1 ;listen.backlog = -1 ; List of ipv4 addresses of FastCGI clients which are allowed to connect. ; Equivalent to the FCGI_WEB_SERVER_ADDRS environment variable in the original ; PHP FCGI (5.2.2+). Makes sense only with a tcp listening socket. Each address ; must be separated by a comma. If this value is left blank, connections will be ; accepted from any ip address. ; Default Value: any ;listen.allowed_clients = any ; Set permissions for unix socket, if one is used. In Linux, read/write ; permissions must be set in order to allow connections from a web server. Many ; BSD-derived systems allow connections regardless of permissions. ; Default Values: user and group are set as the running user ; mode is set to 0666 listen.owner = nobody listen.group = nobody listen.mode = 0666 ; Unix user/group of processes ; Note: The user is mandatory. If the group is not set, the default user's group ; will be used. ; RPM: apache Choosed to be able to access some dir as httpd user = nobody ; RPM: Keep a group allowed to write in log dir. group = nobody ; Choose how the process manager will control the number of child processes. ; Possible Values: ; static - a fixed number (pm.max_children) of child processes; ; dynamic - the number of child processes are set dynamically based on the ; following directives: ; pm.max_children - the maximum number of children that can ; be alive at the same time. ; pm.start_servers - the number of children created on startup. ; pm.min_spare_servers - the minimum number of children in 'idle' ; state (waiting to process). If the number ; of 'idle' processes is less than this ; number then some children will be created. ; pm.max_spare_servers - the maximum number of children in 'idle' ; state (waiting to process). If the number ; of 'idle' processes is greater than this ; number then some children will be killed. ; Note: This value is mandatory. pm = dynamic ; The number of child processes to be created when pm is set to 'static' and the ; maximum number of child processes to be created when pm is set to 'dynamic'. ; This value sets the limit on the number of simultaneous requests that will be ; served. Equivalent to the ApacheMaxClients directive with mpm_prefork. ; Equivalent to the PHP_FCGI_CHILDREN environment variable in the original PHP ; CGI. ; Note: Used when pm is set to either 'static' or 'dynamic' ; Note: This value is mandatory. pm.max_children = 5 ; The number of child processes created on startup. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic' ; Default Value: min_spare_servers + (max_spare_servers - min_spare_servers) / 2 pm.start_servers = 2 ; The desired minimum number of idle server processes. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic' ; Note: Mandatory when pm is set to 'dynamic' pm.min_spare_servers = 1 ; The desired maximum number of idle server processes. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic' ; Note: Mandatory when pm is set to 'dynamic' pm.max_spare_servers = 3 ; The number of requests each child process should execute before respawning. ; This can be useful to work around memory leaks in 3rd party libraries. For ; endless request processing specify '0'. Equivalent to PHP_FCGI_MAX_REQUESTS. ; Default Value: 0 ;pm.max_requests = 500 ; The URI to view the FPM status page. If this value is not set, no URI will be ; recognized as a status page. By default, the status page shows the following ; information: ; accepted conn - the number of request accepted by the pool; ; pool - the name of the pool; ; process manager - static or dynamic; ; idle processes - the number of idle processes; ; active processes - the number of active processes; ; total processes - the number of idle + active processes. ; The values of 'idle processes', 'active processes' and 'total processes' are ; updated each second. The value of 'accepted conn' is updated in real time. ; Example output: ; accepted conn: 12073 ; pool: www ; process manager: static ; idle processes: 35 ; active processes: 65 ; total processes: 100 ; By default the status page output is formatted as text/plain. Passing either ; 'html' or 'json' as a query string will return the corresponding output ; syntax. Example: ; http://www.foo.bar/status ; http://www.foo.bar/status?json ; http://www.foo.bar/status?html ; Note: The value must start with a leading slash (/). The value can be ; anything, but it may not be a good idea to use the .php extension or it ; may conflict with a real PHP file. ; Default Value: not set ;pm.status_path = /status ; The ping URI to call the monitoring page of FPM. If this value is not set, no ; URI will be recognized as a ping page. This could be used to test from outside ; that FPM is alive and responding, or to ; - create a graph of FPM availability (rrd or such); ; - remove a server from a group if it is not responding (load balancing); ; - trigger alerts for the operating team (24/7). ; Note: The value must start with a leading slash (/). The value can be ; anything, but it may not be a good idea to use the .php extension or it ; may conflict with a real PHP file. ; Default Value: not set ;ping.path = /ping ; This directive may be used to customize the response of a ping request. The ; response is formatted as text/plain with a 200 response code. ; Default Value: pong ;ping.response = pong ; The timeout for serving a single request after which the worker process will ; be killed. This option should be used when the 'max_execution_time' ini option ; does not stop script execution for some reason. A value of '0' means 'off'. ; Available units: s(econds)(default), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays) ; Default Value: 0 ;request_terminate_timeout = 0 ; The timeout for serving a single request after which a PHP backtrace will be ; dumped to the 'slowlog' file. A value of '0s' means 'off'. ; Available units: s(econds)(default), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays) ; Default Value: 0 ;request_slowlog_timeout = 0 ; The log file for slow requests ; Default Value: not set ; Note: slowlog is mandatory if request_slowlog_timeout is set slowlog = /var/log/php-fpm/www-slow.log ; Set open file descriptor rlimit. ; Default Value: system defined value ;rlimit_files = 1024 ; Set max core size rlimit. ; Possible Values: 'unlimited' or an integer greater or equal to 0 ; Default Value: system defined value ;rlimit_core = 0 ; Chroot to this directory at the start. This value must be defined as an ; absolute path. When this value is not set, chroot is not used. ; Note: chrooting is a great security feature and should be used whenever ; possible. However, all PHP paths will be relative to the chroot ; (error_log, sessions.save_path, ...). ; Default Value: not set ;chroot = ; Chdir to this directory at the start. This value must be an absolute path. ; Default Value: current directory or / when chroot ;chdir = /var/www ; Redirect worker stdout and stderr into main error log. If not set, stdout and ; stderr will be redirected to /dev/null according to FastCGI specs. ; Default Value: no ;catch_workers_output = yes ; Limits the extensions of the main script FPM will allow to parse. This can ; prevent configuration mistakes on the web server side. You should only limit ; FPM to .php extensions to prevent malicious users to use other extensions to ; exectute php code. ; Note: set an empty value to allow all extensions. ; Default Value: .php ;security.limit_extensions = .php .php3 .php4 .php5 ; Pass environment variables like LD_LIBRARY_PATH. All $VARIABLEs are taken from ; the current environment. ; Default Value: clean env ;env[HOSTNAME] = $HOSTNAME ;env[PATH] = /usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin ;env[TMP] = /tmp ;env[TMPDIR] = /tmp ;env[TEMP] = /tmp ; Additional php.ini defines, specific to this pool of workers. These settings ; overwrite the values previously defined in the php.ini. The directives are the ; same as the PHP SAPI: ; php_value/php_flag - you can set classic ini defines which can ; be overwritten from PHP call 'ini_set'. ; php_admin_value/php_admin_flag - these directives won't be overwritten by ; PHP call 'ini_set' ; For php_*flag, valid values are on, off, 1, 0, true, false, yes or no. ; Defining 'extension' will load the corresponding shared extension from ; extension_dir. Defining 'disable_functions' or 'disable_classes' will not ; overwrite previously defined php.ini values, but will append the new value ; instead. ; Default Value: nothing is defined by default except the values in php.ini and ; specified at startup with the -d argument ;php_admin_value[sendmail_path] = /usr/sbin/sendmail -t -i -f www@my.domain.com ;php_flag[display_errors] = off php_admin_value[error_log] = /var/log/php-fpm/www-error.log php_admin_flag[log_errors] = on ;php_admin_value[memory_limit] = 128M ; Set session path to a directory owned by process user php_value[session.save_handler] = files php_value[session.save_path] = /var/lib/php/session
run.sh
#/bin/bash
IMAGE="leon/php"
Container="php"
Link="mariadb"
docker build -t ${IMAGE} .
docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --name ${Container} --link ${Link}:${Link} ${IMAGE}
这里去创建PHP并启动镜像,需要提到这里的link就是文章开头说到的需要与DB进行安全传输,并在php容器内创建一个DB的host记录。
我们可以使用这个命令去进入容器,查看该记录。
# docker exec -it php bash [root@7e6188415cb2 ansible]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 172.17.0.2 mariadb 29ae9593fbfc 172.17.0.3 7e6188415cb2
Tip: 这里可以看到mariadb的内网ip为172.17.0.2, php-fpm的为172.17.0.3, 我们MAC本机作为Docker主机与容器间会进行DNAT通信,容器因为在同一内网,可自由通信,前提是需要在创建和启动镜像前打开相应服务端口。
Nginx container
这里最终我们会利用Nginx作为一个反向代理,配置www.example.com去访问我们的PHP容器下的Wordpress页面.
Dockerfile
FROM ansible/centos7-ansible/epel:stable ADD ansible /data/ansible WORKDIR /data/ansible RUN ansible-playbook nginx-container.yml -c local VOLUME ["/data/app"] # CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"] ENTRYPOINT [ "/usr/sbin/nginx" ] EXPOSE 80 EXPOSE 443
这里基本与PHP的容器配置类似,执行playbook,共享网站目录,启动nginx服务并打开80,443端口。
ansible/nginx-container.yml
- name: Create Nginx container
hosts: local
vars:
global_conf_path: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
server_conf_path: /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
tasks:
- name: Install epel-release package
yum: name=epel-release state=latest
- name: Install required packages
yum: name={{ item }} state=latest
with_items:
- net-tools
- lsof
- nmap
- nginx
- name: Copy nginx global conf
copy: src=nginx.conf dest={{ global_conf_path }} mode=0644
- name: Copy nginx server conf
copy: src=default.conf dest={{ server_conf_path }} mode=0644
这里安装nginx,并将配置文件复制到对应nginx目录.
ansible/defalut.conf
# The default server
#
upstream backend {
server php:9000;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name http://www.example.com;
root /data/app;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass backend;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
}
ansible/nginx.conf
# For more information on configuration, see: # * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/ # * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/ user nobody; worker_processes 1; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; pid /run/nginx.pid; daemon off; # Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic. include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf; events { worker_connections 768; } http { log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; keepalive_timeout 65; types_hash_max_size 2048; include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; # Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory. # See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include # for more information. include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; server { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server; server_name _; root /usr/share/nginx/html; # Load configuration files for the default server block. include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; location / { } error_page 404 /404.html; location = /40x.html { } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { } } # Settings for a TLS enabled server. # # server { # listen 443 ssl http2 default_server; # listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server; # server_name _; # root /usr/share/nginx/html; # # ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt"; # ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key"; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 10m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # # # Load configuration files for the default server block. # include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; # # location / { # } # # error_page 404 /404.html; # location = /40x.html { # } # # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # location = /50x.html { # } # } }
run.sh
#/bin/bash
IMAGE="leon/nginx"
Container="nginx"
Link="php"
Volume="php"
docker build -t ${IMAGE} .
docker run -d -p 80:80 -p 443:443 --name ${Container} --link ${Link}:${Link} --volumes-from ${Volume} ${IMAGE}
这里需要注意的是我们添加了一个--volumes-from参数用来调用PHP share出来的网站目录。
这里我们分别执行3个目录下的执行脚本(run.sh)后,效果如下:
# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
7e6188415cb2 leon/php "/usr/sbin/php-fpm -F" 2 hours ago Up About an hour 0.0.0.0:9000->9000/tcp php
29ae9593fbfc leon/mariadb "./mariadb.sh" 2 hours ago Up About an hour 0.0.0.0:3306->3306/tcp mariadb
d07bb4aea5c1 leon/nginx "/usr/sbin/nginx" 3 days ago Up 4 hours 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp nginx
# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
leon/php latest f243f43c99a2 3 hours ago 883 MB
leon/mariadb latest 7046c76b434a 3 hours ago 1.694 GB
leon/nginx latest d588d0a73eee 7 days ago 737.6 MB
ansible/centos7-ansible stable 5108f665e079 3 weeks ago 433.3 MB
到这里我们就成功创建并启动了我们Wordpress所需要的三个基础服务。
我们可以利用Docker start "容器名"或者Docker stop "容器名" 去启动或者关闭这个包含具体服务的容器,可以作为我们在Docker服务器下重启服务的命令。
如果需要进入容器进行调测,我们也可以使用Docker exec -it "容器名" bash
测试结果
我们给MAC主机添加一个host记录
# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 http://www.example.com
然后使用PHP测试文件分别测试PHP是否部署成功以及PHP与MariaDB是否联通
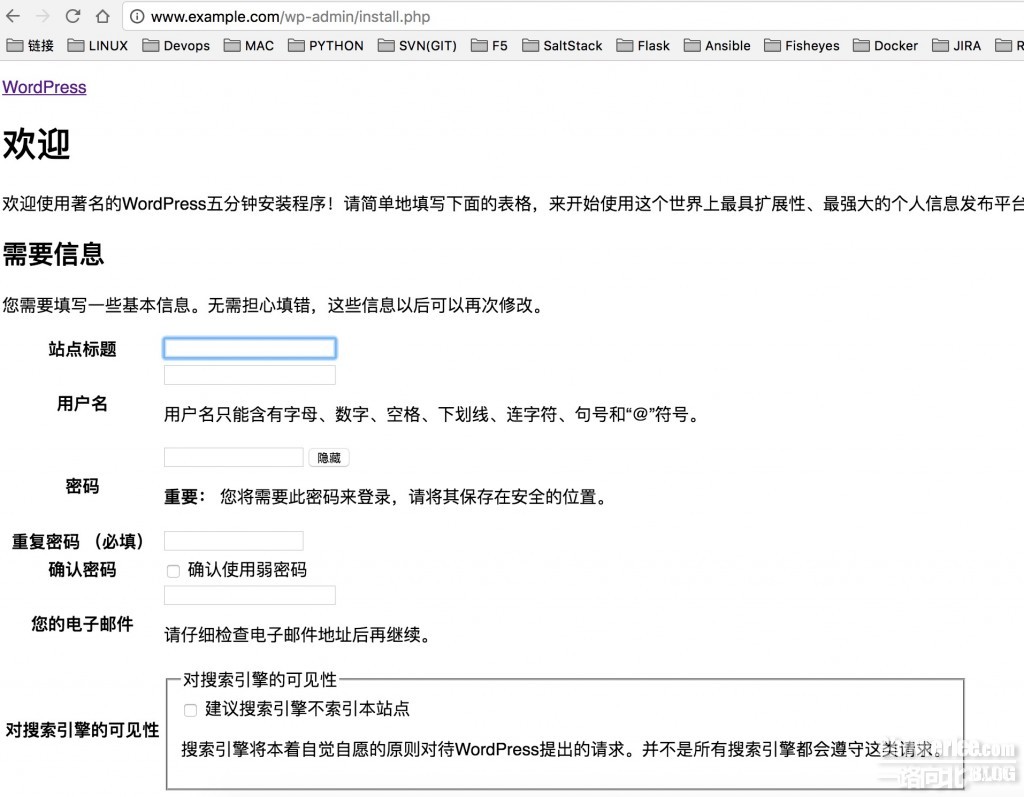
最终我们访问www.example.com查看wordpress是否部署成功。
至此使用Docker+Ansible部署Wordpress大功告成。。。