Create .Net Core Api controller for CRUD with repository
In the previous article, I introduced how to use the repository pattern, at this time, I will show you how to use for CURD with the Api controller.
We need to create the controller for implement the RESTful Api, so first of all, we need to know what’s that!
1. What’s RESTful Api
REST stands for Representational State Transfer, and it is an architectural style for building web services. A RESTful API is a web service that follows the principles of REST.
A RESTful API is characterized by the following properties:
- Client-server architecture: Separation of concerns between the client and the server.
-
Stateless: Each request from a client to the server contains all the information necessary for the server to understand the request. The server does not store any client context between requests.
-
Cacheable: Clients can cache responses to improve performance.
-
Uniform interface: A set of well-defined HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) is used to interact with resources, and resources are identified by URIs.
-
Layered system: A client can’t tell whether it is connected directly to the end server or communicating through an intermediary, such as a load balancer.
-
Code on demand (optional): Servers can transfer executable code to clients, such as JavaScript, to be executed in the client’s context.
In practice, a RESTful API typically provides a set of endpoints that clients can use to interact with the resources exposed by the API. For example, a RESTful API for a blog might provide endpoints for creating, updating, and deleting blog posts, and for retrieving a list of blog posts or a single blog post by ID.
2. Create the Api Controller
2.1. What’s Route
Route is an attribute that can be applied to an action method in a controller to specify the URL pattern that the action method should respond to. In other words, it defines the route template for the action method.
The Route attribute can be also used to specify the route template directly on an action method, like this:
[HttpGet("users/{id}")]
public IActionResult GetUser(int id)
{
// ...
}
In this example, the HttpGet attribute specifies that the action method should handle HTTP GET requests, and the users/{id} URL pattern specifies that the method should handle requests for URLs that match the /users/{id} pattern, where {id} is a placeholder for the ID of the user being requested.
Alternatively, you can specify the route template at the controller level using the Route attribute on the controller class, and then specify additional path segments for individual actions using the HttpGet, HttpPost, etc. attributes. Here’s an example:
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class UserController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public IActionResult GetUser(int id)
{
// ...
}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult CreateUser([FromBody] User user)
{
// ...
}
}
In this example, the Route attribute specifies that all action methods in the UserController should be mapped under the /api/users URL path. The HttpGet and HttpPost attributes specify the additional path segments and HTTP methods for the GetUser and CreateUser methods, respectively.
2.2 Create the Api Methods
Ok, let’s create out controller and methods. As the previous article mention, we need to create an ApiResult object for handle return data. After that, we can use C# Extensions to help to create an UserController
We need to update the constructor for setup(inject) the Repository object
// MyDemo/Controllers/UserController.cs
[ApiController]
[Route("api")]
public class UserController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IUserRepository _userRepository;
public UserController(IUserRepository userRepository)
{
this._userRepository = userRepository;
}
}
For better user friend the Api Url, I just set the controller router attribute to “api“, that’s mean don’t need to add the controller name in the api url
The first Api method is GetUsers, that’s mean we need to get more than one users, and use the HttpGet attribute for specify this is a Get method
/// <summary>
/// Get all users
/// Api Url: http://website-domain/api/users (without controller name)
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpGet("users")]
public async Task<ActionResult<IEnumerable<User>>> GetUsers()
{
var apiResult = new ApiResult<IEnumerable<User>>();
try
{
apiResult.Data = await _userRepository.GetAllAsync();
return Ok(apiResult);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
apiResult.Success = false;
apiResult.Message = ex.Message;
return StatusCode(500, apiResult);
}
}
Create a *Get* method GetUser for get single user
/// <summary>
/// Get user by id
/// Api Url: http://website-domain/api/user/id (without controller name)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpGet("user/{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<User>> GetUser(int id)
{
var apiResult = new ApiResult<User>();
try
{
apiResult.Data = await _userRepository.GetItemWithConditionAsync(u => u.Id == id);
return Ok(apiResult);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
apiResult.Success = false;
apiResult.Message = ex.Message;
return StatusCode(500, apiResult);
}
}
Create a *Post* method PostUser for create user, we need to check the user name whether exist before create the new one
/// <summary>
/// Create a user
/// Api Url: http://website-domain/api/user (without controller name)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="user"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpPost("user")]
public async Task<ActionResult<User>> PostUser(User user)
{
var apiResult = new ApiResult<Object>();
try
{
var isExist = await _userRepository.UserIsExist(user.Name);
if (isExist)
{
apiResult.Success = false;
apiResult.Message = "The user has already exists!";
}
else
{
_userRepository.Create(user);
await _userRepository.SaveAsync();
}
return Ok(apiResult);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
apiResult.Success = false;
apiResult.Message = ex.Message;
return StatusCode(500, apiResult);
}
}
Create a *Put* method PutUser for update user
/// <summary>
/// Update the user
/// Api Url: http://website-domain/api/user (without controller name)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
/// <param name="user"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpPut("user")]
public async Task<ActionResult<User>> PutUser(User user)
{
var apiResult = new ApiResult<Object>();
//if the id is 0, then don't allow to update it
if (user.Id == 0)
{
return BadRequest();
}
try
{
//get the current DB user
var dbUser = await _userRepository.GetItemWithConditionAsync(u => u.Id == user.Id);
if (dbUser == null)
{
apiResult.Success = false;
apiResult.Message = "Can't found the user!";
}
else
{
//update the user
_userRepository.Update(user);
await _userRepository.SaveAsync();
}
return Ok(apiResult);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
apiResult.Success = false;
apiResult.Message = ex.Message;
return StatusCode(500, apiResult);
}
}
In the end, create the Delete method DeleteUser for delete the user by id
/// <summary>
/// Delete user
/// Api Url: http://website-domain/api/user/id (without controller name)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpDelete("user/{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteUser(int id)
{
var apiResult = new ApiResult<Object>();
try
{
var dbUser = await _userRepository.GetItemWithConditionAsync(u => u.Id == id);
if (dbUser == null)
{
apiResult.Success = false;
apiResult.Message = "Can't found the user!";
}
else
{
//delete the user
_userRepository.Delete(dbUser);
await _userRepository.SaveAsync();
}
return Ok(apiResult);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
apiResult.Success = false;
apiResult.Message = ex.Message;
return StatusCode(500, apiResult);
}
}
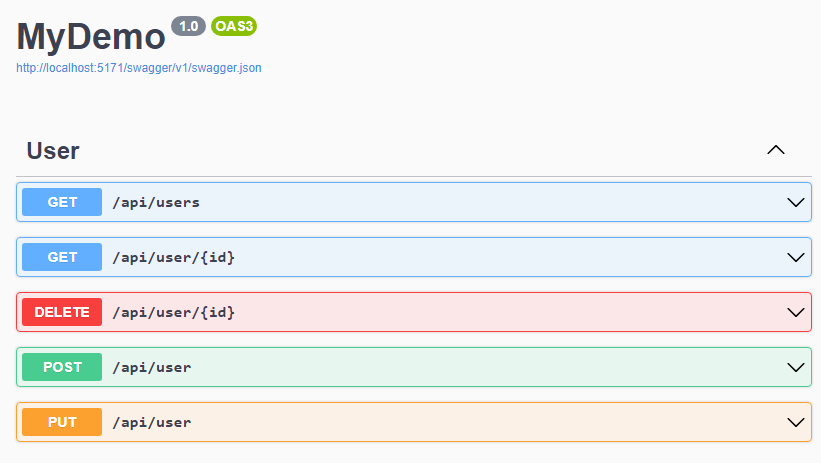
Ok, for now, we have finished the CRUD methods for RESTful API, let’s try them through swagger. There are 5 APIs show in the swagger page:
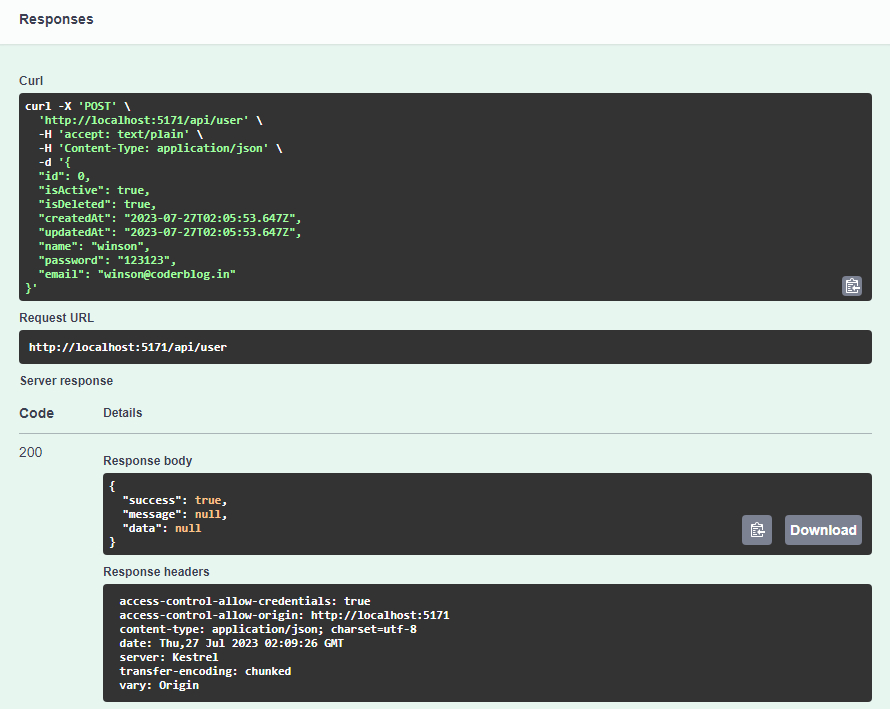
First, we try to create a user with POST method. Pass the below data to API
It will return the below information, the success flag is true and there is no error message, that’s mean the record has been created!
we can check the database
That’s cool! Ok, let try to get the data
and we got the data with our AipResult object format.
well, I try to create more data as below for test get user by id
and try to get the id = 2 items
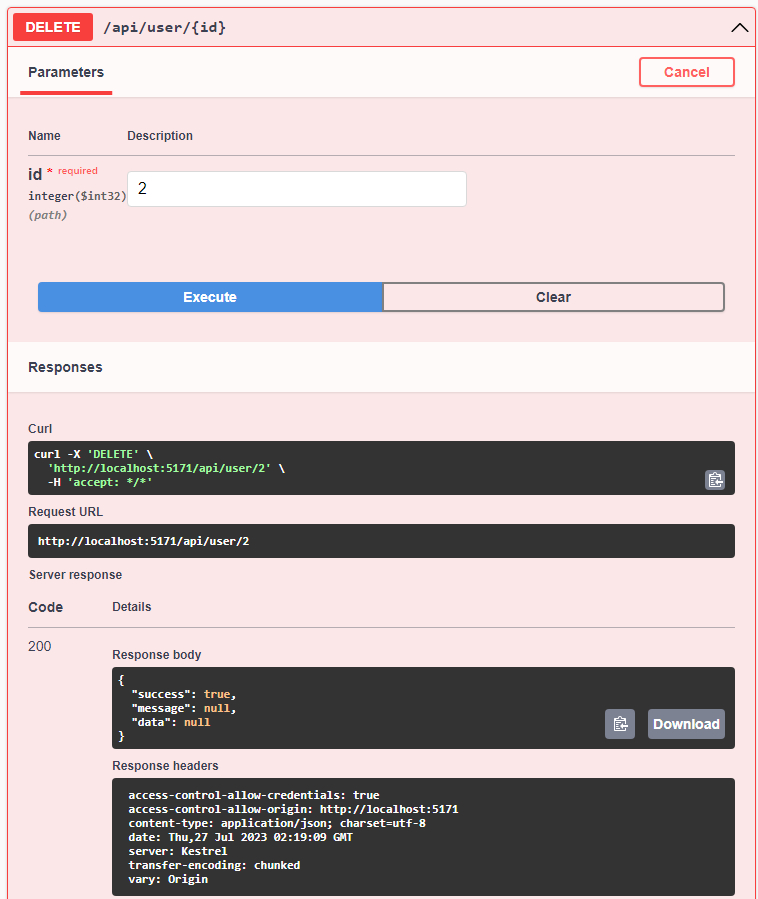
That’s great, it’s working! The last testing to try to delete an user by id
and check the database data
Everything is fine! 🙂
3. Summarize
We talked about what’s RESTful API and how to create it. But there is one thing we still need to improve, for the complete system, we should need to handle the event/error logs, this can help us to trace the error or some outstanding issue, so in the next, we will discus how to do it! :smirk:
![]()
The post Create .Net Core Api controller for CRUD with repository first appeared on Coder Blog.