Batch Norm, Layer Norm, Instance Norm, Group Norm
lufficc发表于 2020-05-27 23:12:33
自 Batch Normalization 从 2015 年被 Google 提出来之后,又诞生了很多 Normalization 方法,如 Layer Normalization, Instance Normalization, Group Normalization。 这些方法作用、效果各不相同,但却有着统一的内核和本质:计算输入数据在某些维度上的方差和均值,归一化,最后用可学习参数映射归一化后的特征。这可以统一表达为:
\[y = \frac{x - \mathrm{E}[x]}{ \sqrt{\mathrm{Var}[x] + \epsilon}} * \gamma + \beta\]我们以图像数据为例子,给定输入数据 $x \in (N, C, H, W)$, 其中 $N, C, H, W$ 分别为 batch size, 通道数,图像高和宽。
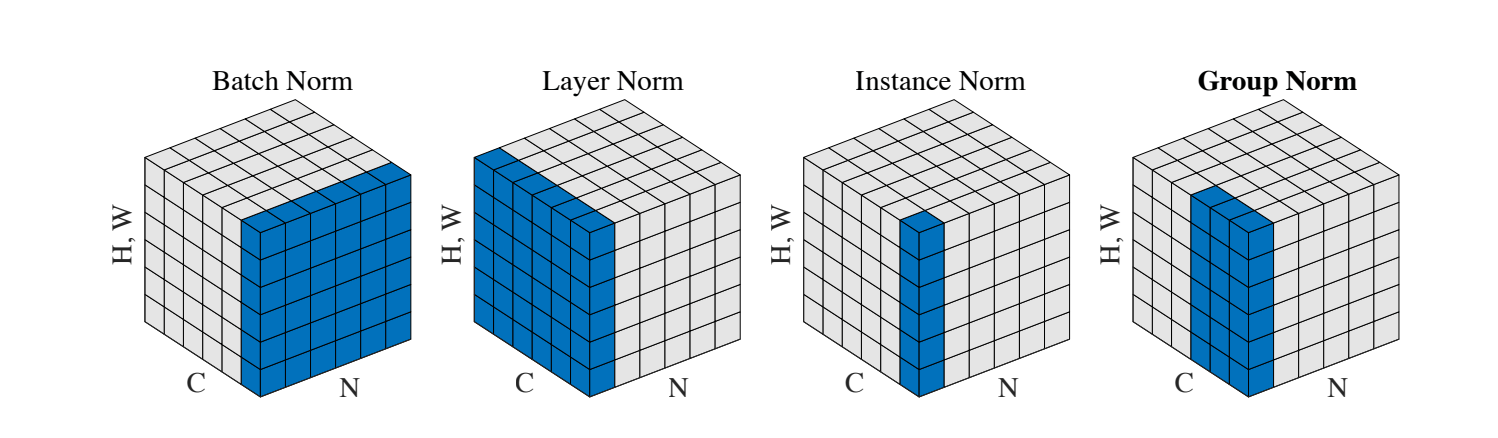
如上图所示,BN 计算在 $N, H, W$ 维度上的均值方差,LN 计算在 $C, H, W$ 维度上的均值方差,IN 计算在 $H, W$ 维度上的均值方差,GN 计算在 $C’, H, W$ 维度上的均值方差,其中 $C’$ 是分组后的通道个数。
计算维度的不同是这些方法的唯一区别。也正是因为计算维度的不同,也导致了不同的效果和特性。
- BN 计算依赖 $N, H, W$,因此当 batch size 较小时效果可能并不理想,且 batch size 对结果影响较大。
- IN 计算依赖 $H, W$,不依赖 batch size, 相当于计算每个单独的 instance 不同通道的特征,IN 也因此常用于风格转换。
- LN 计算依赖 $C, H, W$,舍弃了对 batch size 的依赖,因此常用在 batch size 变化的模型中,如 RNN。另外 LN 与 BN 和 IN 不同的是,BN 和 IN 整个通道用的是同一个标量进行映射,而 LN 通道内每一个元素都采用不同的标量进行映射。因此前者可学习参数的形状为 $(C)$, 而 LN 可学习参数的形状为 $(C \times H \times W)$。
- GN 首先将通道分组 $(N, C, H, W) \rightarrow (N, G, C’, H, W)$(其中$C’ = \frac{C}{G}$),计算依赖 $C’, H, W$, 显然不依赖 batch size。而将特征分组,有点类似将类似特征归一化(比形状、亮度和纹理等),实验证明 GN 效果很好。而且事实上,GN 可以看作是 IN 和 LN 的中间体:当分组个数等于 1 时相当于不分组,是计算 $C, H, W$ 上的均值方差,而当分组个数等于通道个数时($G = C$),相当于计算在 $H, W$ 上的均值方差,于是退化成了 IN。
我们可以很轻松的用 PyTorch 实现每个方法的等效版本:
BN
inputs = torch.randn(5, 256, 32, 32) # (N, C, H, W)
bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(256) # Weight shape: (C, )
# weight default is 1
bn.weight.data = torch.rand_like(bn.weight)
# compute on (N, H, W)
var, mean = torch.var_mean(inputs, dim=(0, 2, 3), keepdim=True, unbiased=False) # (1, C, 1, 1)
std = (var + bn.eps).sqrt() # (1, C, 1, 1)
norm = (inputs - mean) / std # (N, C, H, W)
print(torch.allclose(
norm * bn.weight.view(1, 256, 1, 1) + bn.bias.view(1, 256, 1, 1),
bn(inputs))
) # True
IN
inputs = torch.randn(5, 256, 32, 32) # (N, C, H, W)
ins = nn.InstanceNorm2d(256, affine=True) # Weight shape: (C, )
# weight default is 1
ins.weight.data = torch.rand_like(ins.weight)
# compute on (H, W)
var, mean = torch.var_mean(inputs, dim=(2, 3), keepdim=True, unbiased=False) # (N, C, 1, 1)
std = (var + ins.eps).sqrt() # (N, C, 1, 1)
norm = (inputs - mean) / std # (N, C, H, W)
print(torch.allclose(
norm * ins.weight.view(1, 256, 1, 1) + ins.bias.view(1, 256, 1, 1),
ins(inputs))
) # True
LN
inputs = torch.randn(5, 256, 32, 32) # (N, C, H, W)
normalized_shape = inputs.shape[1:] # Normalize on (C, H, W)
ln = nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape)
# weight default is 1
ln.weight.data = torch.rand_like(ln.weight)
# compute on (C, H, W)
var, mean = torch.var_mean(inputs, dim=(1, 2, 3), keepdim=True, unbiased=False) # (N, 1, 1, 1)
std = (var + ln.eps).sqrt() # (N, 1, 1, 1)
norm = (inputs - mean) / std # (N, C, H, W)
print(torch.allclose(norm * ln.weight + ln.bias, ln(inputs))) # True
GN
inputs = torch.randn(5, 256, 32, 32) # (N, C, H, W)
num_groups = 32
bn = nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=num_groups, num_channels=256) # Weight shape: (C, )
# weight default is 1
bn.weight.data = torch.rand_like(bn.weight)
grouped_inputs = inputs.view(5, num_groups, 256 // num_groups, 32, 32) # (N, G, C', H, W)
# compute on (C', H, W)
var, mean = torch.var_mean(grouped_inputs, dim=(2, 3, 4), keepdim=True, unbiased=False) # (N, G, 1, 1, 1)
std = (var + bn.eps).sqrt() # # (N, G, 1, 1, 1)
norm = (grouped_inputs - mean) / std # (N, G, C', H, W)
print(torch.allclose(
norm.view(5, 256, 32, 32) * bn.weight.view(1, 256, 1, 1) + bn.bias.view(1, 256, 1, 1),
bn(inputs))
) # True