思科策略路由
Teacher Du发表于 2024-11-01 03:51:26
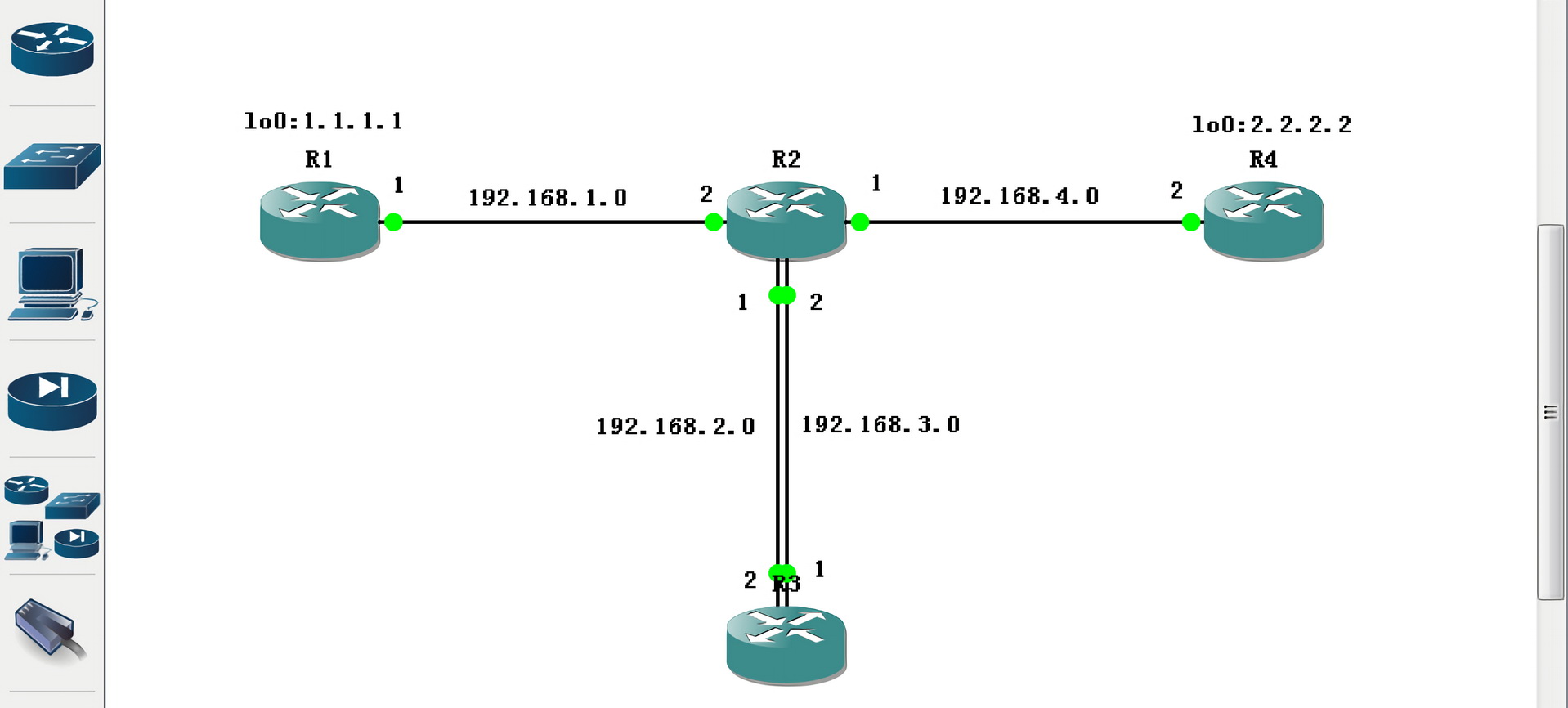
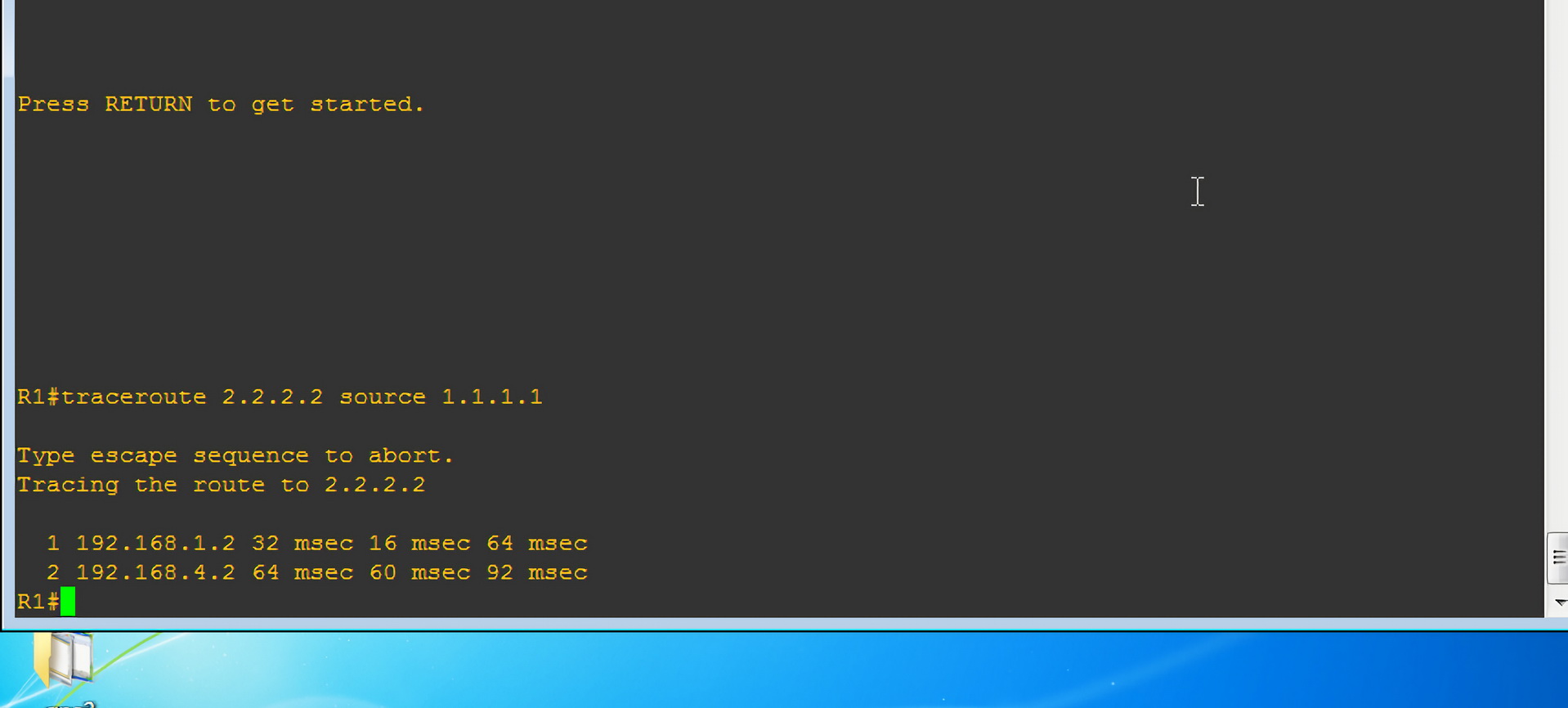
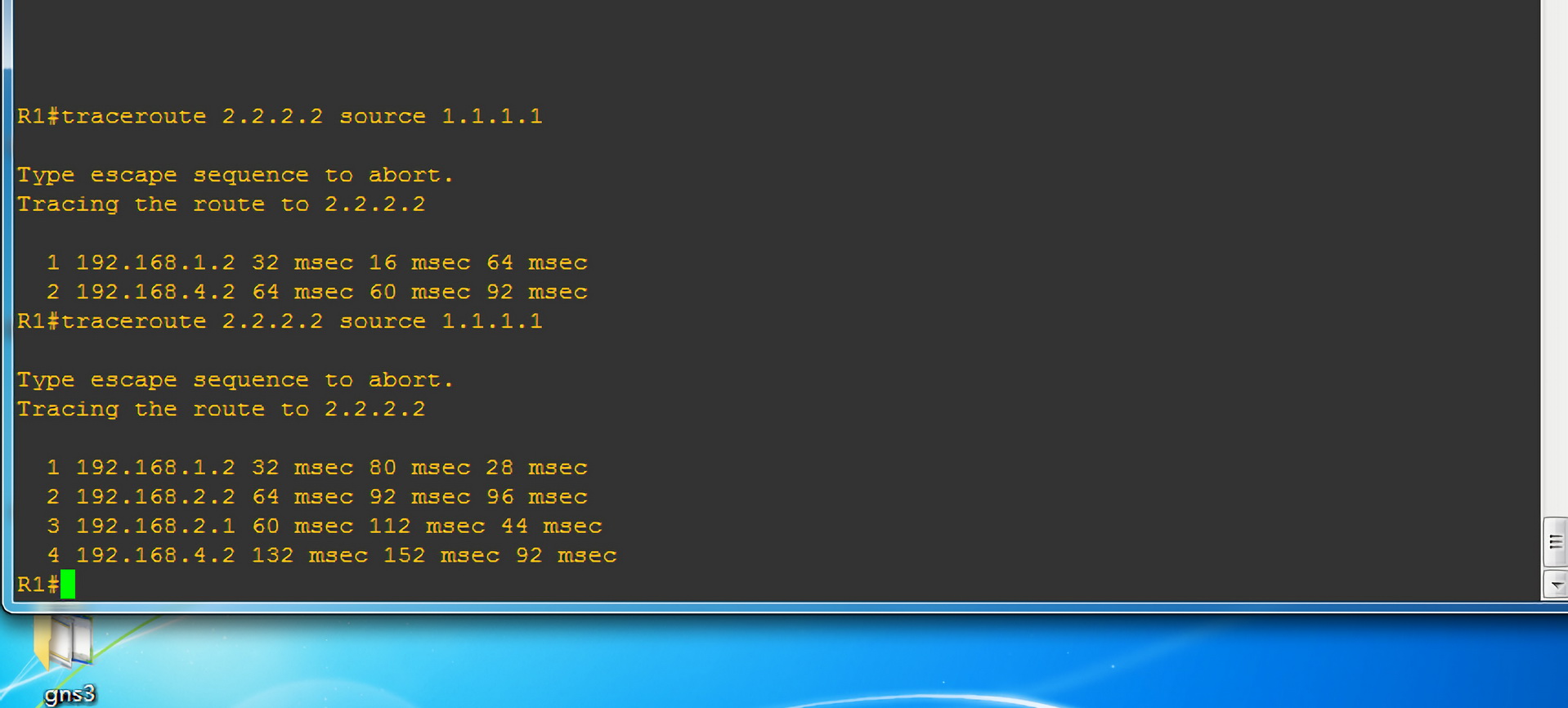
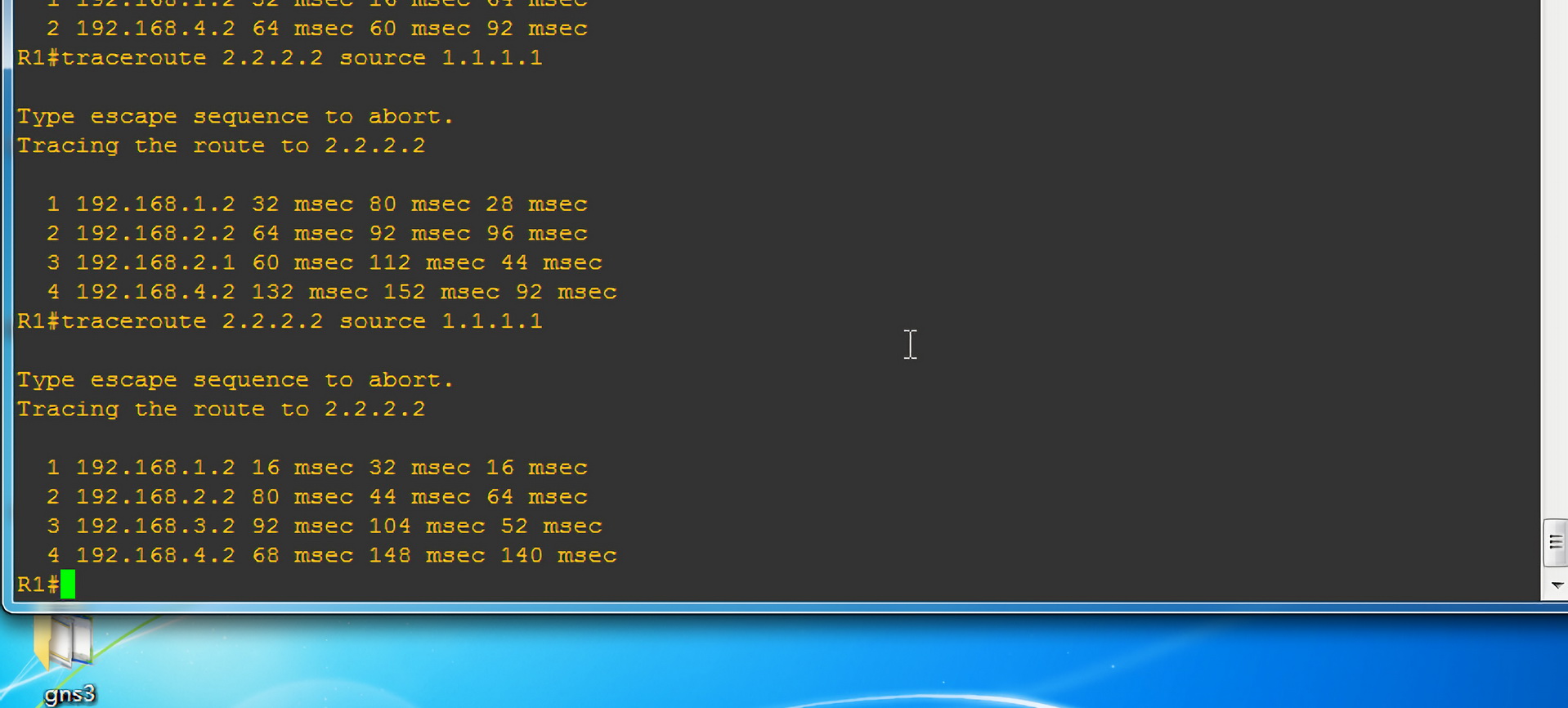
两点之间直线最短,故图中 R1 如果与 R4 通信,只通过 R2 路由是最快的。但今天我们任性下,让数据包经过 R3 路由器,再发往 R4。
数据走向
我们需要数据包的发送走向:
- 192.168.1.2
- 192.168.2.2
- 192.168.3.2
- 192.168.4.2
我们需要数据包的接受走向:
- 192.168.3.1
- 192.168.1.1
操作命令
1 | R4#configure terminal |
注意:首先我们需要配置基础网络环境,实现全网连通。「仅以 R4 路由器为例」配置如上。
修改走向
1 | R2(config)#access-list 100 permit ip host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2 |
注意:接下来我们修改一下数据包走向。通过拓扑我们可以判断,数据包在 R2 路由器需要转变方向,发送给 R3,所以我们在 R2 路由进行如上配置。
变更走向
R3(config)#access-list 100 permit ip host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2
R3(config)#route-map p2 permit 10
R3(config-route-map)#match ip address 100
R3(config-route-map)#set ip next-hop 192.168.3.2
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#ip policy route-map p2
注意:我们需要在 R3 配置。